Explore ESS
Discover more about the European Spallation Source: what it is, how it works and why it matters.
ESS (full name: European Spallation Source ERIC) is a research facility under construction in Lund (Sweden), with its data management and software centre located outside Copenhagen (Denmark).
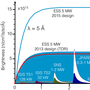
When completed, ESS will be the world’s most powerful accelerator-based source of neutrons. Scientists will use these particles to study the properties and behaviour of materials - right down to the level of atoms.
Funded by 13 European countries*, this big-science facility is built with contribution from more than 40 research institutes in Europe, and with knowledge and know-how from many research centres worldwide. ESS attracts people from diverse fields and cultures who share the excitement of building a state-of-the-art facility to enable great science and innovation for a sustainable world.
The construction of the facility is ongoing. Follow the progress of the ESS Road to Science on our social media.
You can also follow our live public operations screen that shows the status of parts of the machine as they become operational.
*Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Norway, Poland, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom
Every year, thousands of researchers from academia and industry will use the ESS facility to learn more about materials, unlocking discoveries and driving innovative solutions to address some of humanity’s biggest challenges in energy, health and the environment.
With the help of neutrons, scientists will be able to understand materials and matter at a deeper level than ever before, investigating deep inside objects, obeserving where the atoms are and how they behave. This can help researchers design new materials for better batteries, greener plastics or stronger engineering structures. Or, it could help life science researchers develop new vaccines or more effective medicines.
Up to 3,000 researchers from around the world will come to ESS each year to carry out experiments on samples of the materials they are studying. Many will also visit MAX IV Laboratory, the neighbouring synchrotron light source, where they can get complementary data about their samples using X-rays.
At ESS, scientists will carry out research in the following areas:
|
|
Life Sciences |
|
Magnetism & Superconductivity |
|
Soft-Condensed Matter |
|
Engineering & Geo-Sciences |
|
|
Chemistry of Materials |
|
Energy Research |
|
Fundamental & Particle Physics |
|
Archaeology & Heritage Conversation |
Future Science
Curious about the future science at ESS? Read more here.
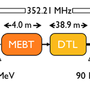
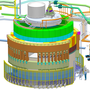
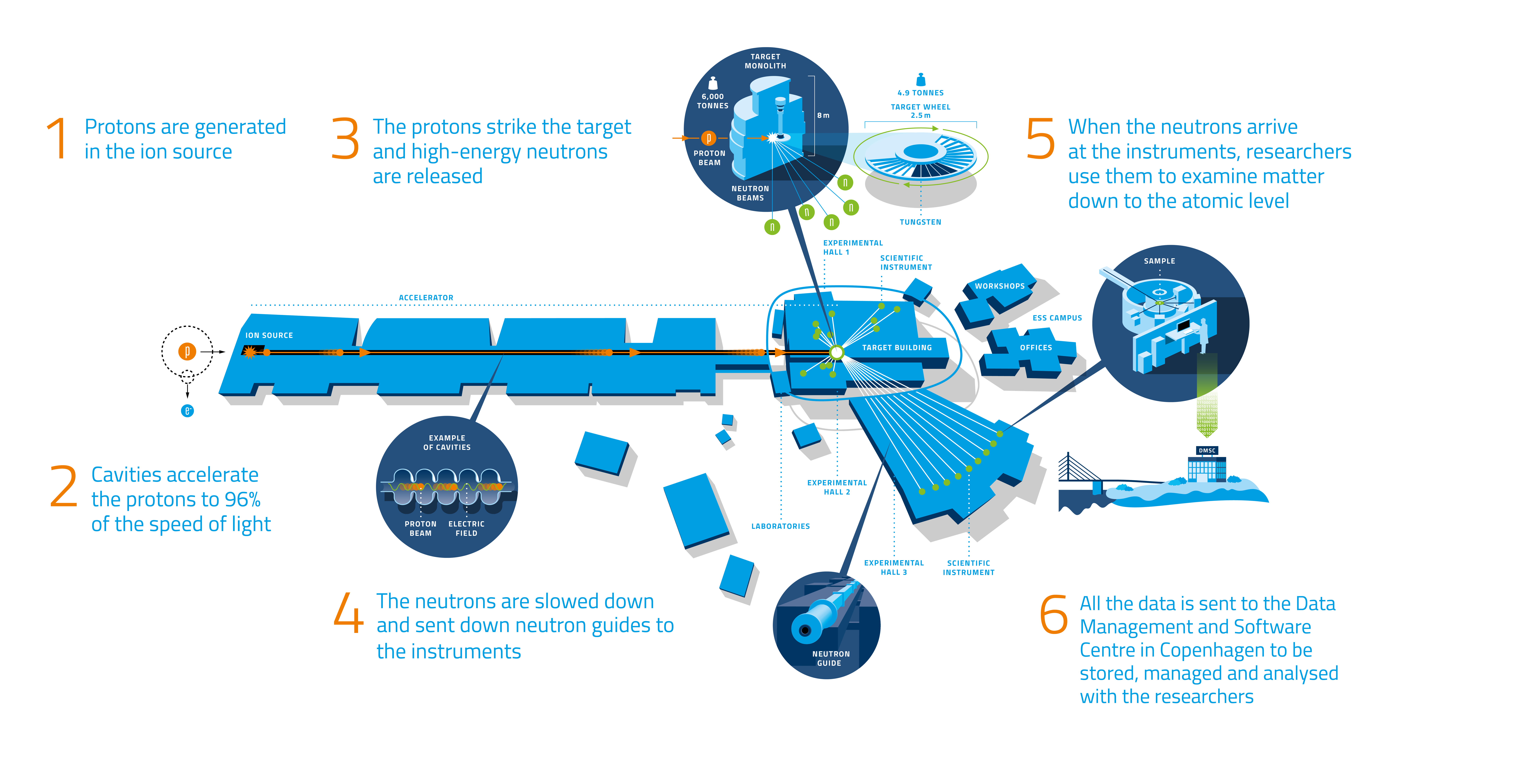
ESS is an accelerator-based neutron source designed to provide a large number of neutrons with the right energy for the researchers to use.
Neutrons are generated through a process called spallation and then slowed down to the desired energy and guided to the scientific instruments, as shown below.
Neutron instruments use different technologies to investigate various properties of materials.
Resources for teachers
Downloadable materials
| Other materials
|
Online seminarsHere we will tell you when there are interesting online seminars coming up: Join Prof. Malik Maaza to explore the neutron’s role in physics, its impact on the Standard Model & cosmology, and advances with Fabry-Pérot resonators! Title: “Quantum Trapping of Cold Neutrons with Picosecond Precision"Date: Thursday March 27, 2025Time: 16:00 CET (11:00 EDT) - (Please note the daylight-saving time adjustment in the USA). A unique feature of a neutron is that it sensitive to the four fundamental interactions of particles: strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational. This multi-sensitivity makes neutron wave-matter optics a particularly versatile tool for testing quantum mechanics and fundamental physics concepts in general. The lifetime of a free neutron defined via its beta-decay is of pivotal importance within cosmology and the accuracy of this lifetime measurement is central to the standard model of particle physics. The two major methods used to measure free neutron lifetimes give different values. One method was shown to give enhanced accuracy if cold neutrons are trapped in so-called Fabry-Perot resonators. This webinar will reveal more, while covering topics such as the de Broglie wave-particle duality, Fermi total reflection phenomenon, tunneling and trapping of cold neutrons. This event is open to the public, so don't miss out! Secure your spot by REGISTER HERE (to receive the Zoom link promptly and to receive the recording. This series is open to all, so feel free to share) This series is open to all, so feel free to share The colloquia series, "Physics for Development," is organized by the Forum on International Physics (FIP) at the American Physical Society (APS). You can explore the archive of PHYSICS MATTERS Colloquia Series Colloquia Series whenever it suits you. Discover International Engagement page | Activities near Lund and CopenhagenHere we will inform you of relevant in-person activities in the Lund or Copenhagen areas Sunday 6 April, 14:30 - 15:15 Stadsbiblioteket, Gothenburg Neutrons show the way: A talk at the International Science Festival Gothenburg by Sindra Petersson Årsköld, Senior Advisor Please note: The talk will be in Swedish. Swedish description below. Vad är European Spallation Source? Hur fungerar det och framför allt: vilken forskning kommer att bedrivas där? Neutroner låter oss undersöka materien, förstå fysik och kemi och visa vägen till nya läkemedel, smarta material, kvantsystem och mycket mera. ESS, the European Spallation Source, är Sveriges största forskningssatsning genom tiderna och en av Europas största just nu. Anläggningen byggs i Lund, med 13 medlemsländer och i samarbete med flera svenska universitet, och ska öppna för forskning 2027. https://www.vetenskapsfestivalen.se/for-alla/neutroner-visar-vagen/6849/
|
DISCOVER | FOLLOW | SHARE