The first in-situ conditioning of a Spoke Cryomodule in the ESS Superconducting Linac marks a significant step towards preparation to the full accelerator operation and the Beam on Dump milestone.
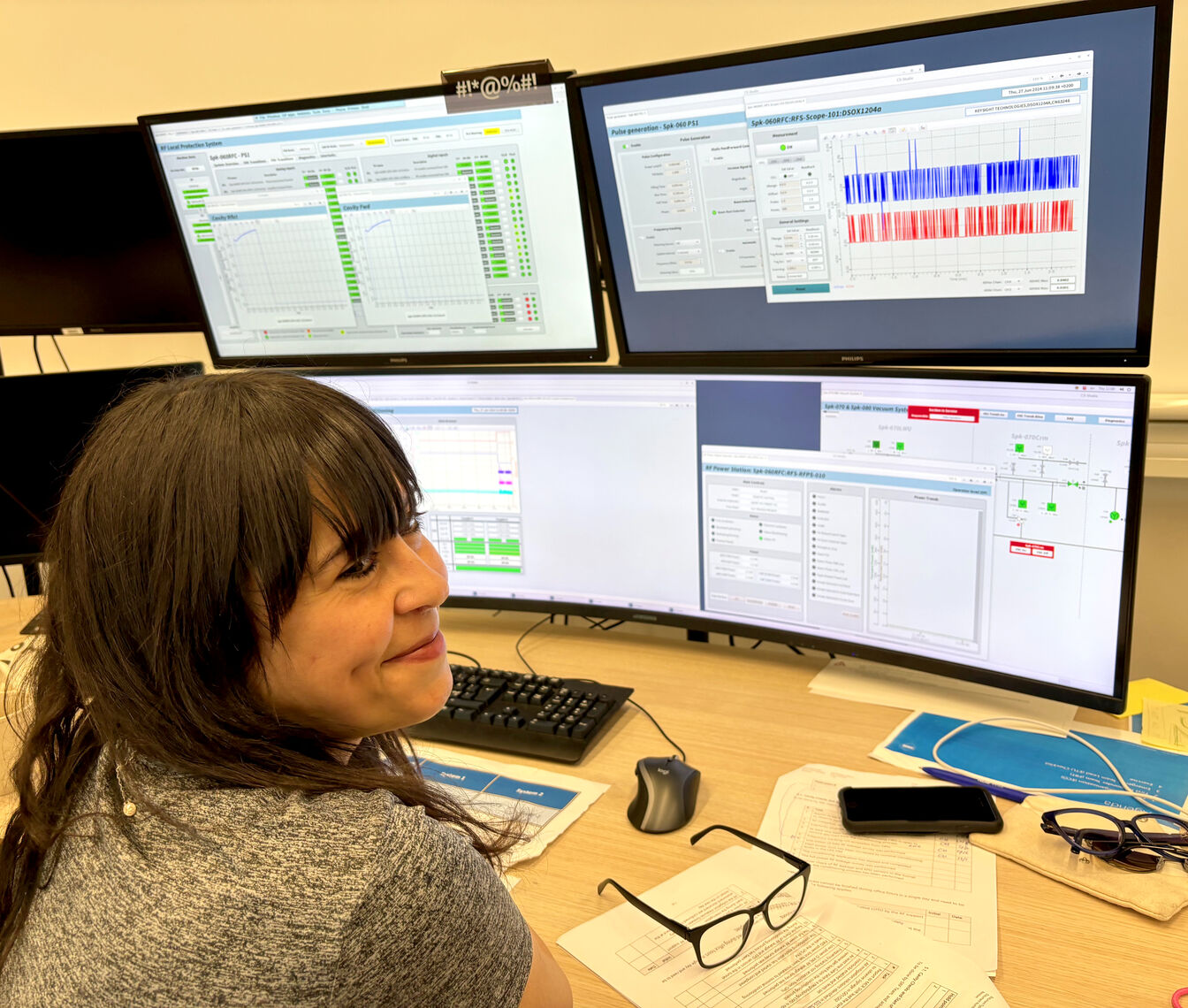
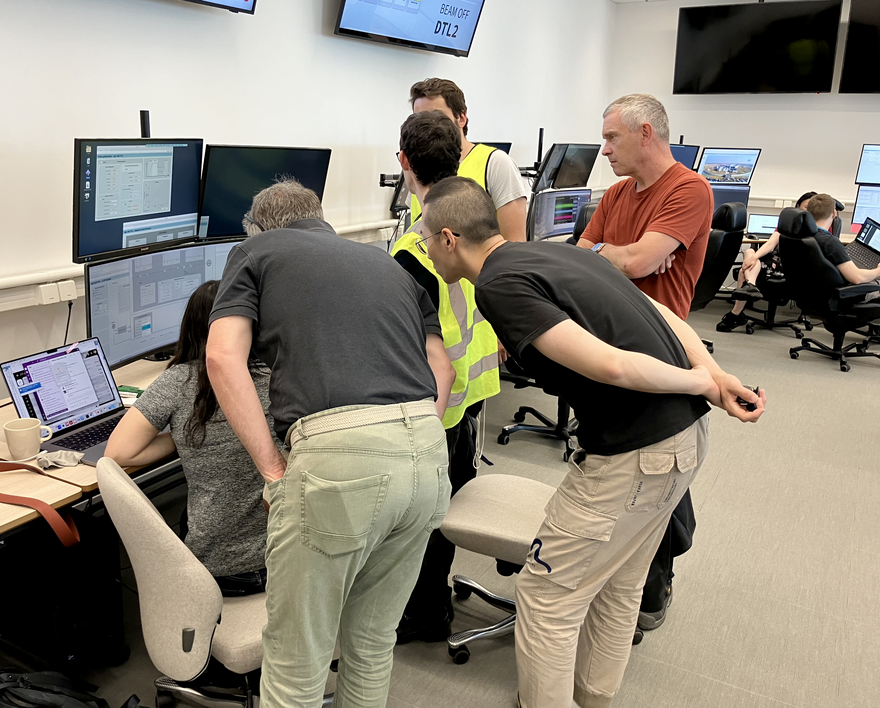
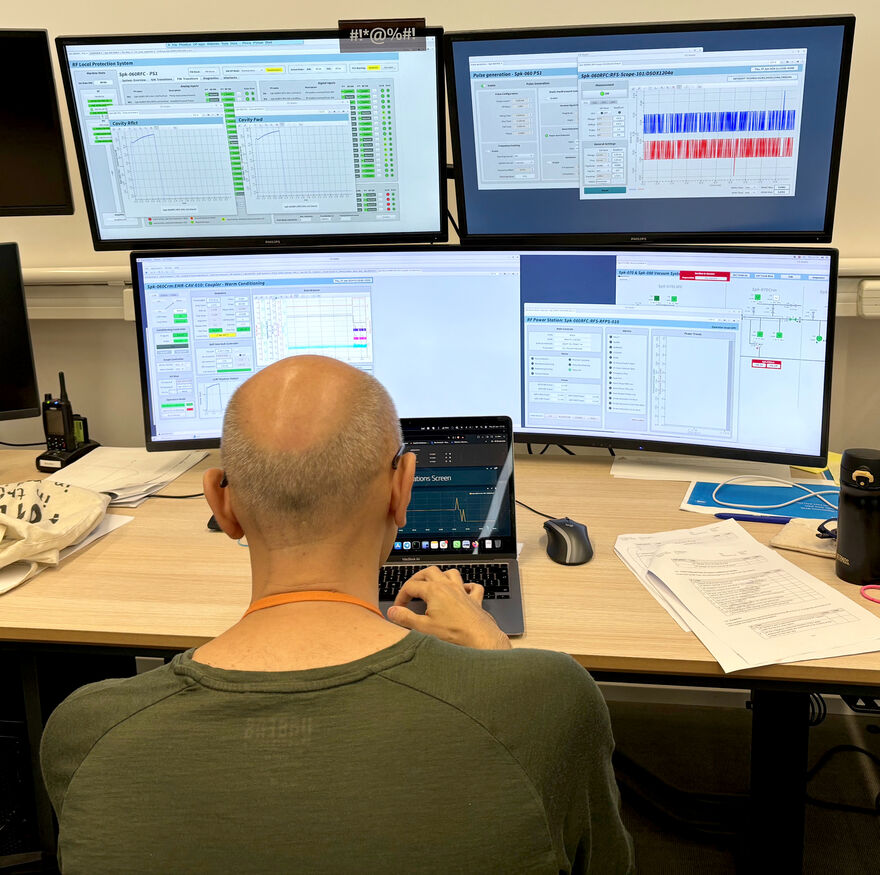
On Friday, June 28, a significant milestone was reached in the ESS superconducting linac. For the first time, warm coupler conditioning in a Spoke Cryomodule was performed in-situ, in the Accelerator tunnel. The achievement, which saw a Radio-frequency (RF) pulse transmitted from an RF power station in the Gallery building through the RF distribution system to a power coupler in a fully installed Spoke Cryomodule, marks the beginning of a thorough conditioning process that will encompass all accelerating components along the superconducting linac, preparing their operation. This crucial step, executed successfully, involved collaborative efforts from the RF, Superconducting RF and Power Converters teams, ICS controls, Radiation Protection, the ESS vacuum team and the ESS Main Control Room.
At midday on Thursday, a sense of excitement filled the air as operators, accelerator technicians, engineers, and scientists witnessed the first RF power ramp-up sequence deployed for a power coupler in a spoke cryomodule in the tunnel. This significant achievement follows months of meticulous preparation, which included setting up and testing the RF power sources, connecting and testing the cryomodule and its infrastructure, and deploying the necessary controls. The milestone is particularly impressive given that detailed preparations began nearly two years ago, aimed at implementing mitigating measures to safely carry out this work without restricting worker access to the whole tunnel. This accomplishment marks a crucial step towards achieving the ESS Beam on Dump (BoD) milestone.
During the power coupler conditioning stage, RF power is gradually sent to the system systematically increasing its average power (by regulating RF pulse length, peak power, and repetition rates), in order to gradually prepare the RF surfaces to sustain high power operation and desorb the gases from the surfaces. RF pulses start with the shortest possible pulse and increase in power until the maximum is reached. This process is repeated with several pulse lengths until the nominal ESS RF pulse length is achieved. A similar process will be performed after the accelerator cooldown this coming autumn, tuning the cavities to their nominal frequency and gradually exposing the surfaces to RF operation and bringing each cavity to its nominal operating point, ready to accelerate the beam.
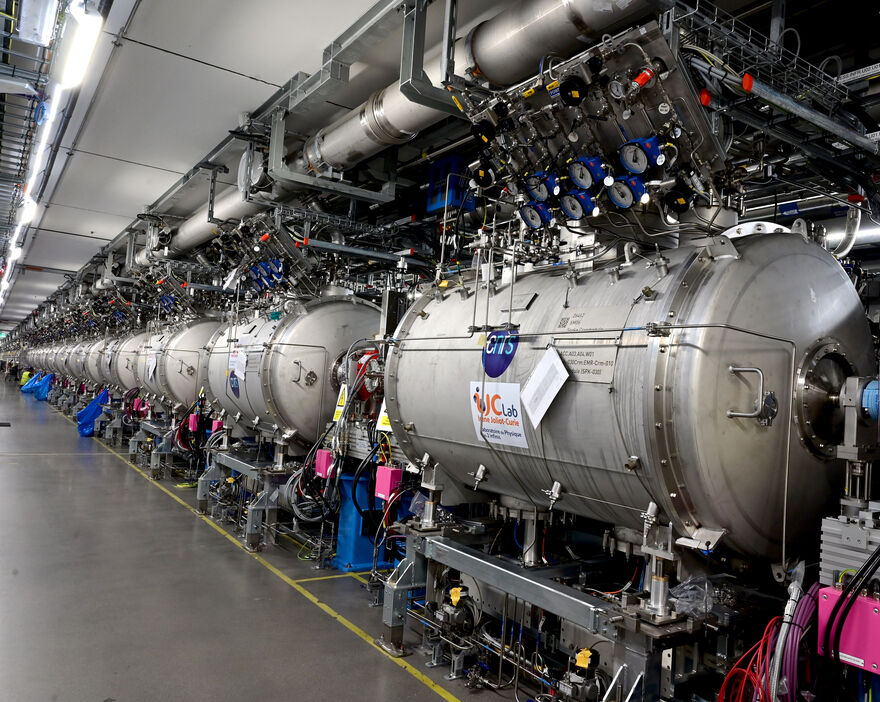
The warm coupler conditioning of the first cryomodule was completed on Tuesday July 2, setting the stage for the serial conditioning of all cavities along the superconducting linac, which is set to start in August. To date, 26 out of the 27 cryomodules needed for BoD and Beam on Target (BoT) are in place in the tunnel, with the final cryomodule scheduled for installation in mid-July.