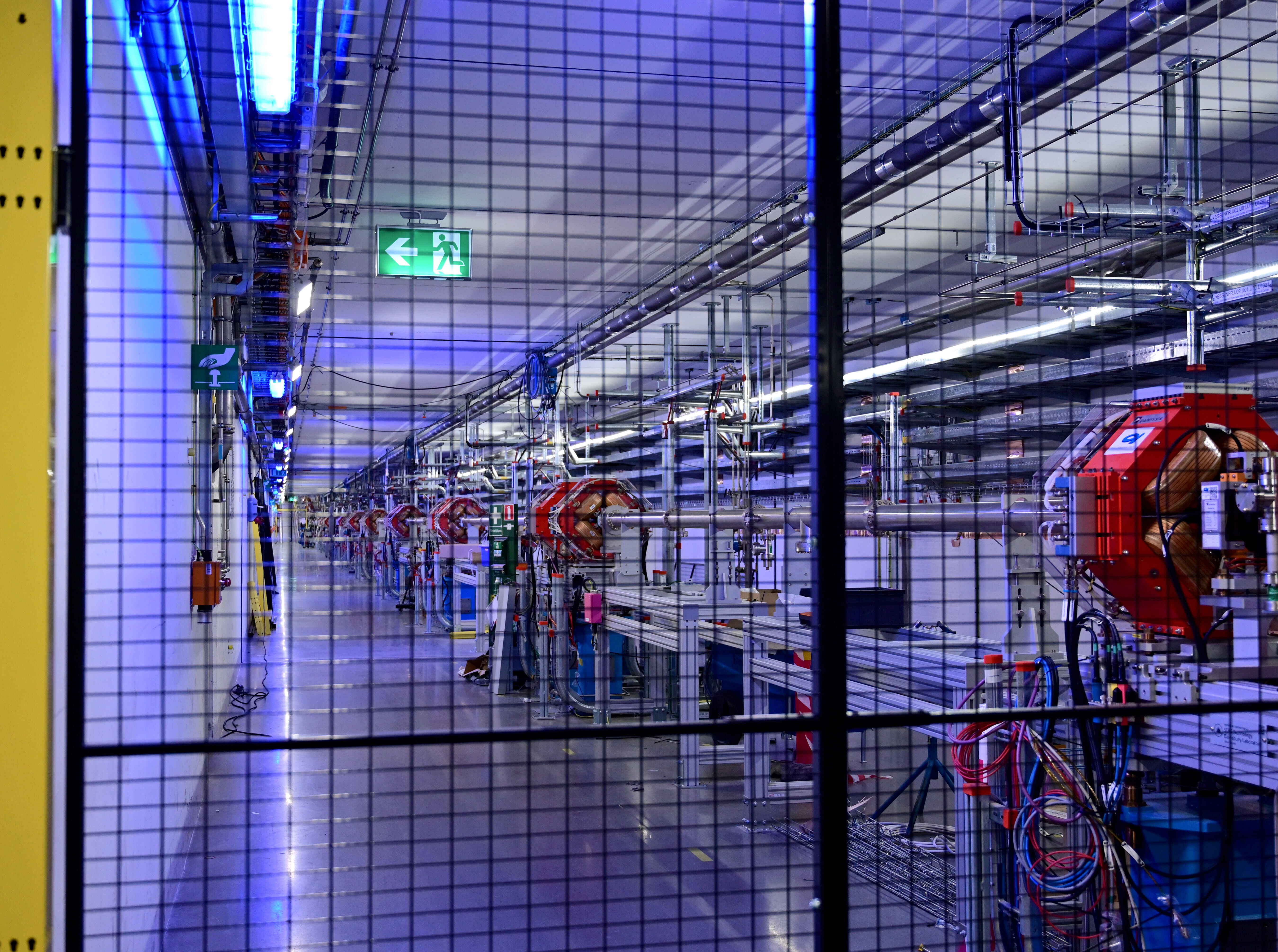
ESS has successfully completed the verification and validation of two critical safety systems: the Personnel Safety System (PSS) and the Oxygen Deficiency Hazard Detection System (ODHDS). These systems are now operational, ensuring the safe commissioning and operation of the ESS accelerator. This milestone, led by the Protection Systems Group (PSG) within the Integrated Control System (ICS) division, was essential for beginning key activities like accelerator cooldown and RF conditioning.
What Do These Systems Do?
The PSS protects personnel from hazards such as ionising radiation, high voltage, and other risks within the accelerator tunnel, ensuring safe access and operations. The ODHDS, part of the Gas Detection Systems, monitors oxygen levels to prevent risks associated with helium depletion in confined spaces.
Installation and Scale
The installation of these systems spanned several years supporting the staged installation and commissioning of the accelerator and its sub-systems, and included:
- Integration of 400 systems and subsystems.
- Over 3,000 input/output signals across the 600-metre-long accelerator and klystron gallery.
- Installation of more than 230 electrical enclosures and 60 km of copper cables and optical fibres.
- Two access stations regulating personnel and material entry into the accelerator tunnel.
Rigorous Testing
The development of safety-critical systems like PSS and ODHDS - including setting requirements, design, procurement, installation, verification, and validation - follows a stringent lifecycle based on two main pillars: the ESS Engineering Management Handbook and IEC 61511, a functional safety standard that defines the framework, definitions, system, hardware, and application programming requirements for safety-instrumented systems.
The verification of the systems was carried out in multiple stages examining the system in detail. This included:
- Functional testing of individual assemblies.
- Hardware installation checks on-site.
- Application program and software validation in simulations and peer reviews.
- Integrated hardware-software testing in the production environment.
Over 8,000 test cases were conducted during six weeks of final integration testing, ensuring every component met stringent functional and safety requirements.
Next Steps
The PSS team is continuing the effort to install safety systems to other critical areas, including the Target, bunker, and Experimental Halls, to support upcoming Beam on Target operations. These systems include PSS, advanced gas detection systems and laser safety interlocks.
A Collaborative Achievement
The development of these systems was an in-house effort, complemented by contributions from external experts from other particle accelerator facilities as well as Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW), who performed an independent functional safety assessment.
With the safety systems now operational in the accelerator, ESS can ensure a safe and efficient working environment in the tunnel and gallery as we progress towards full commissioning and, ultimately, Beam on Target.