ESS has successfully completed its first integration test of the entire neutron data acquisition system, connecting a BIFROST neutron detector module to the ESS timing system and control network.
Thermalised neutron events were detected, processed, and stored, marking a significant milestone in ESS commissioning efforts.
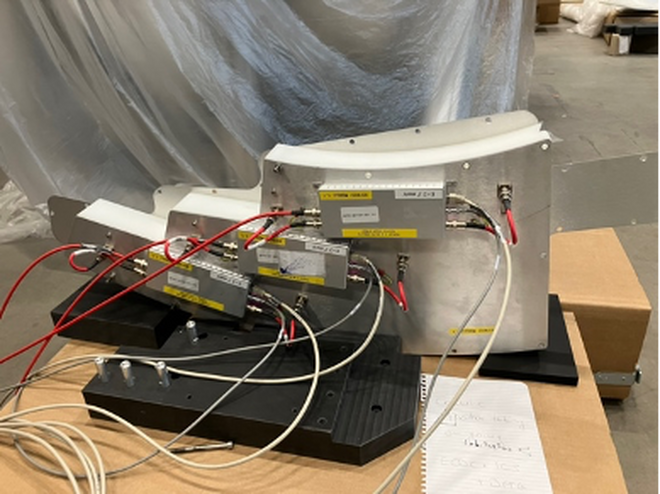
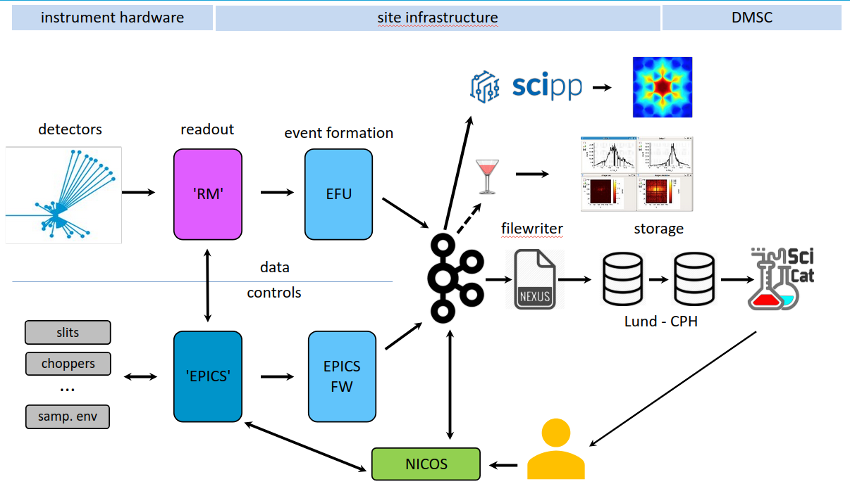
For the first time, an ESS neutron detector module was successfully connected to the ESS timing system and integrated control network. Thermalised neutrons from a radioactive source were detected by the module, processed using the Event Formation Unit (EFU) software running on a dedicated server in the ESS on-site server hall, and stored in a NeXus file. This test covered the entire neutron data acquisition system and was performed as a BIFROST detector readout end-to-end trial, resulting in data being visualised using tools provided by the ESS Data Management & Software Centre (DMSC). An overview of this system is provided below (Fig. 1).
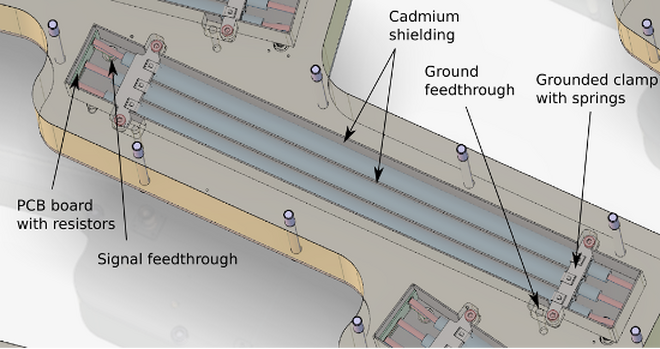
For the test, a single BIFROST detector module was used (Fig.2), comprised of three interconnected He-3 Tube triplets that function as a single long position-sensitive detector (Fig.3). Neutron signals were amplified by preamplifiers and digitised by the Front-End Node (FEN), which added timing information and formatted the data. The Readout Master Module (RMM) forwarded this data to the EFU, which transformed the digital geometry into a logical map by calculating pixel positions, and created neutron events based on calculations of the relative time of arrival of the neutron within the ESS time frame. Finally, the EFU streamed the processed data to a Kafka broker, where the Filewriter software stored it in a NeXus file as an experiment record.
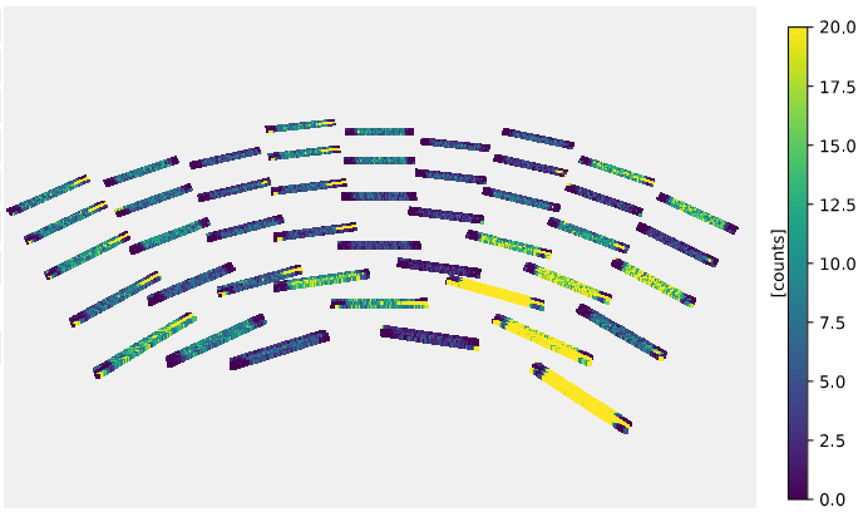
Initial tests detected cosmic-ray neutrons at one event per minute, verifying the functionality of the system. With a radioactive AmBe neutron source provided by the Radiation Protection Team, neutron events increased to 25 per second, allowing detailed testing of all FEN channels. Data visualisation confirmed accurate connections between the logical and physical detector geometry throughout the entire data chain (Fig. 4).
The setup, configuration and troubleshooting of this system required:
- The NICOS instrument control system, provided by the Experimental Control & Data Curation (ECDC) team, which handled file-writing control, metadata capture and experiment control
- Neutron Instrument and Technologies Integration Support (NITIS), with firmware developed by the Detector Group FPGA development team, managed EPICS integration for RMM and FEN configuration
- Network connectivity and data storage, with contributions from IT/CGI, and DMSC teams.
- Data evaluation, led by the Instrument Data Scientist at DMSC.
The test was run as part of the BIFROST Instrument project, aligning with established safety, on-site testing, and troubleshooting processes. This milestone validates the ESS data acquisition architecture and lays the groundwork for future commissioning activities.