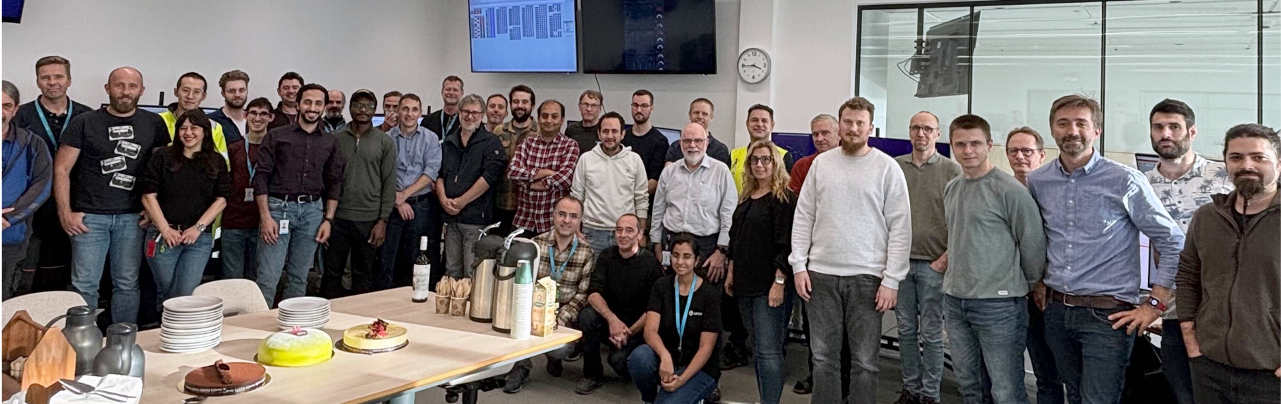
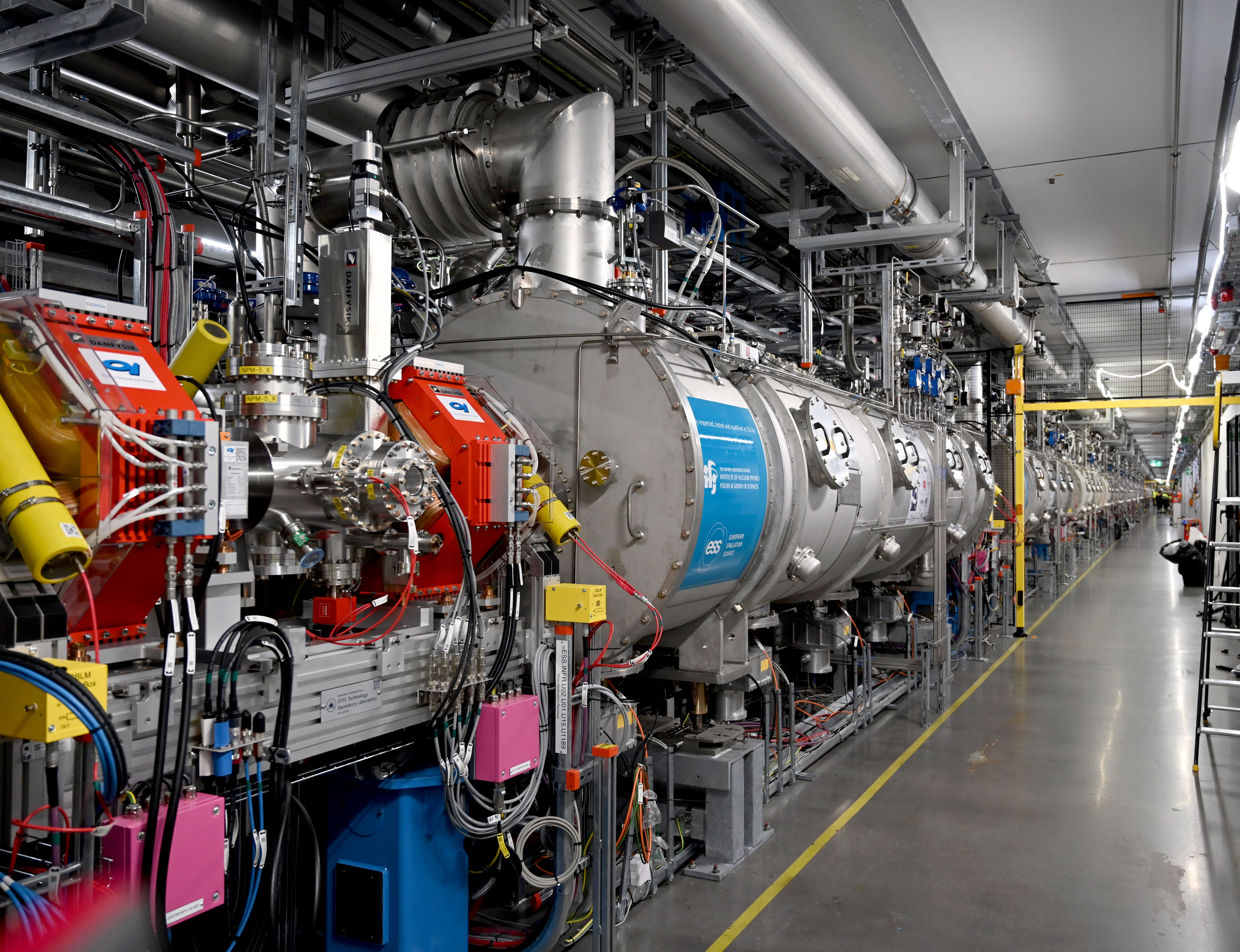
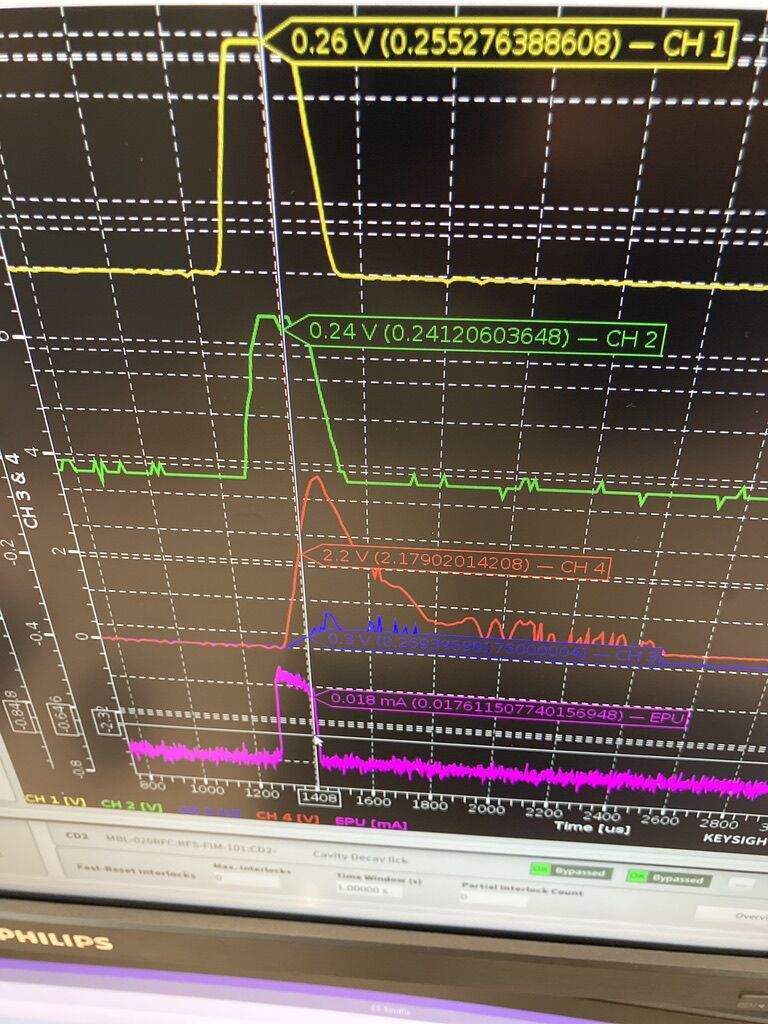
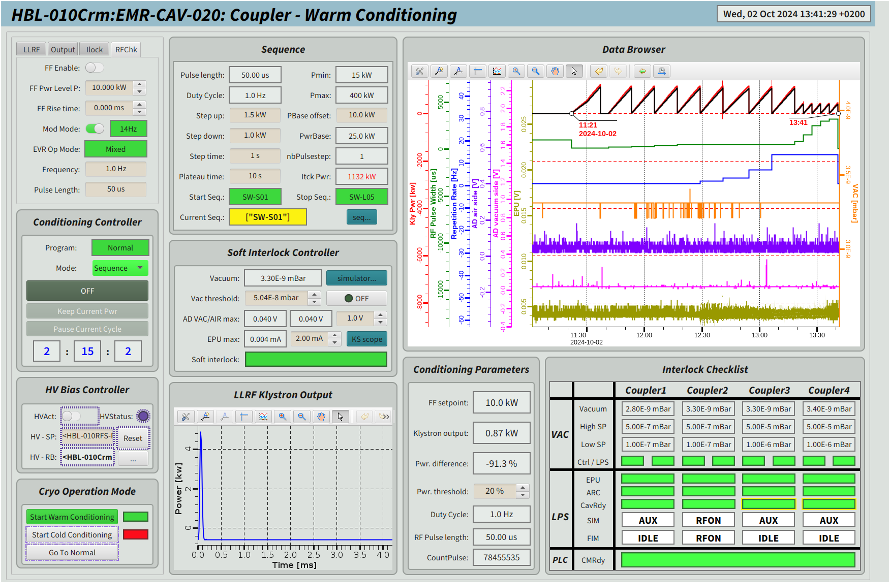
With the completion of the warm conditioning of all 82 couplers in the spoke, medium beta and high beta sections, all 27 cryomodules in the superconducting linac (SCL) section of the ESS accelerator have been declared ready for cooldown.
The warm coupler conditioning started in June this year, with the first coupler in the spoke section receiving the first radio-frequency (RF) pulse. Thanks to extensive collaboration between multiple teams and partner institutions, this crucial phase was successfully completed on October 18, setting the stage for the start of cold operation of the linac.
Coupler conditioning is a critical step in the integration of multiple, independently tested systems. It involves synchronising cryomodules, RF systems, power converters, vacuum systems, cooling infrastructure, and control software, ensuring they operate in harmony with local protection systems to safeguard the correct configuration of the accelerator's components. This phase not only verifies the hardware's performance but also provides a valuable opportunity for procedural testing and cross-team training, essential in preparation for beam commissioning in 2025.
In the coming weeks, efforts will shift towards preparing the machine for cooldown. This will involve completing the commissioning of the backup compressor, conducting final leak checks on all cryogenic lines, verifying control systems, and completing pre-start reviews. The cold conditioning process will begin once all 27 cryomodules reach a stable temperature of 2K in the tunnel, marking the final step before the cavities can be declared ready for beam operations.
This milestone represents a substantial collaborative achievement, with contributions from various teams across ESS and its partner institutions. The elliptical cryomodules (medium and high beta) were assembled at CEA (France), and the spoke cryomodules at IJCLab (France), with cavities provided by INFN (Italy), STFC (UK), and IJCLab. The spoke cryomodules underwent testing at the FREIA lab at Uppsala University (Sweden), and the elliptical cryomodules were tested at an on-site test stand, in close collaboration with IFJPan (Poland). The conditioning process was led by the Linac Group in the Accelerator Division, with significant support from the RF, Power Converters, and Vacuum Groups, as well as Controls in ICS, Radiation Protection (RP), and the Main Control Room (MCR) in Operations.
This achievement is a significant step toward ESS assuming full ownership of these critical accelerator components for reliable facility operations.
This spotlight article is part of the series "Road to Beam on Dump" where we highlight all the systems required to commission the ESS accelerator.
Previous updates:
- ESS Linac Under Vacuum
- The Power to Accelerate: RF Power Stations up and running
- Installation and Testing of the 2 MW RF Scope Completed
- Focus on Beam Instrumentation: Completion of Beam Current Monitors Installation in the ESS Accelerator
- First Insertable Beam Stop installed in the ESS superconducting linac
- Magnets Ready to Focus and Steer the Proton Beam
- Warm Coupler Conditioning starts in the ESS Superconducting Linac