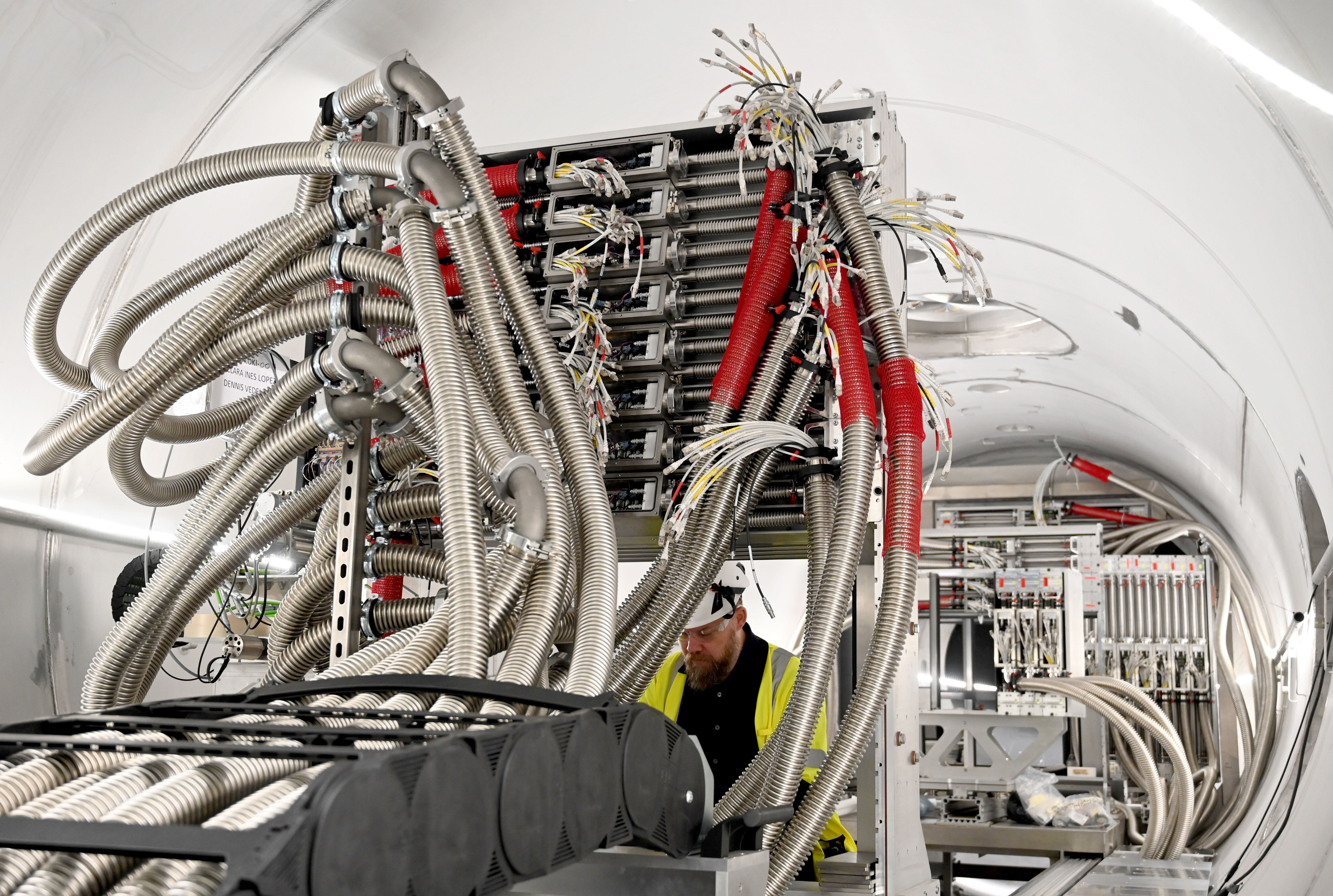
Utgård, the ESS off-site detector laboratory, is home to pioneering work on detector technology, which is crucial to the facility’s mission of becoming the next European flagship facility for neutron research.
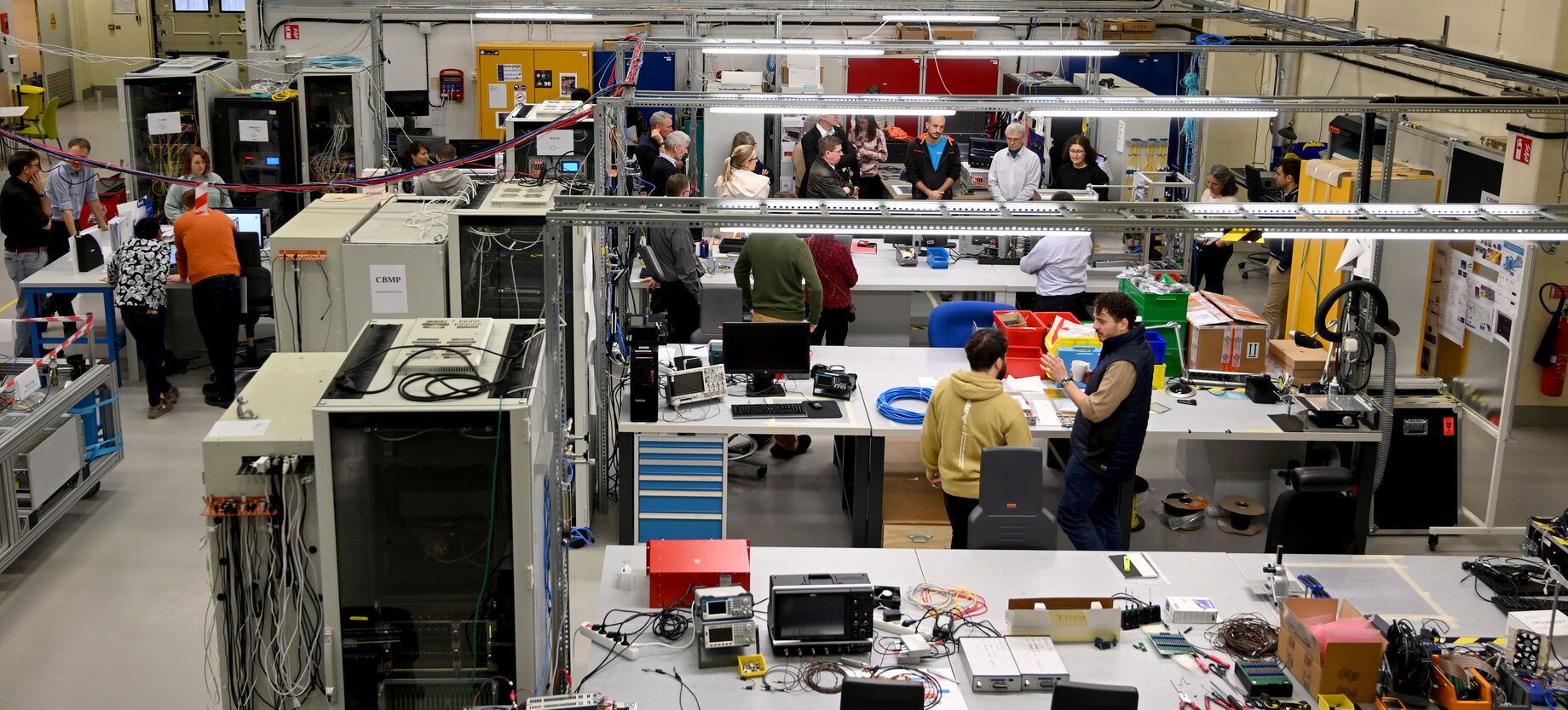
Utgård serves as the development, assembly, and testing hub for neutron detectors that will be installed on ESS’s 15 scientific instruments and test beamline.
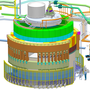
Within this 1,300-square-metre workshop, ESS engineers, technicians, and detector scientists collaborate to design, assemble, and test neutron detectors produced in-house, as well as to conduct testing and integration of detectors developed and delivered by ESS In-Kind partners.
Next-Generation Multi-Blade Detectors
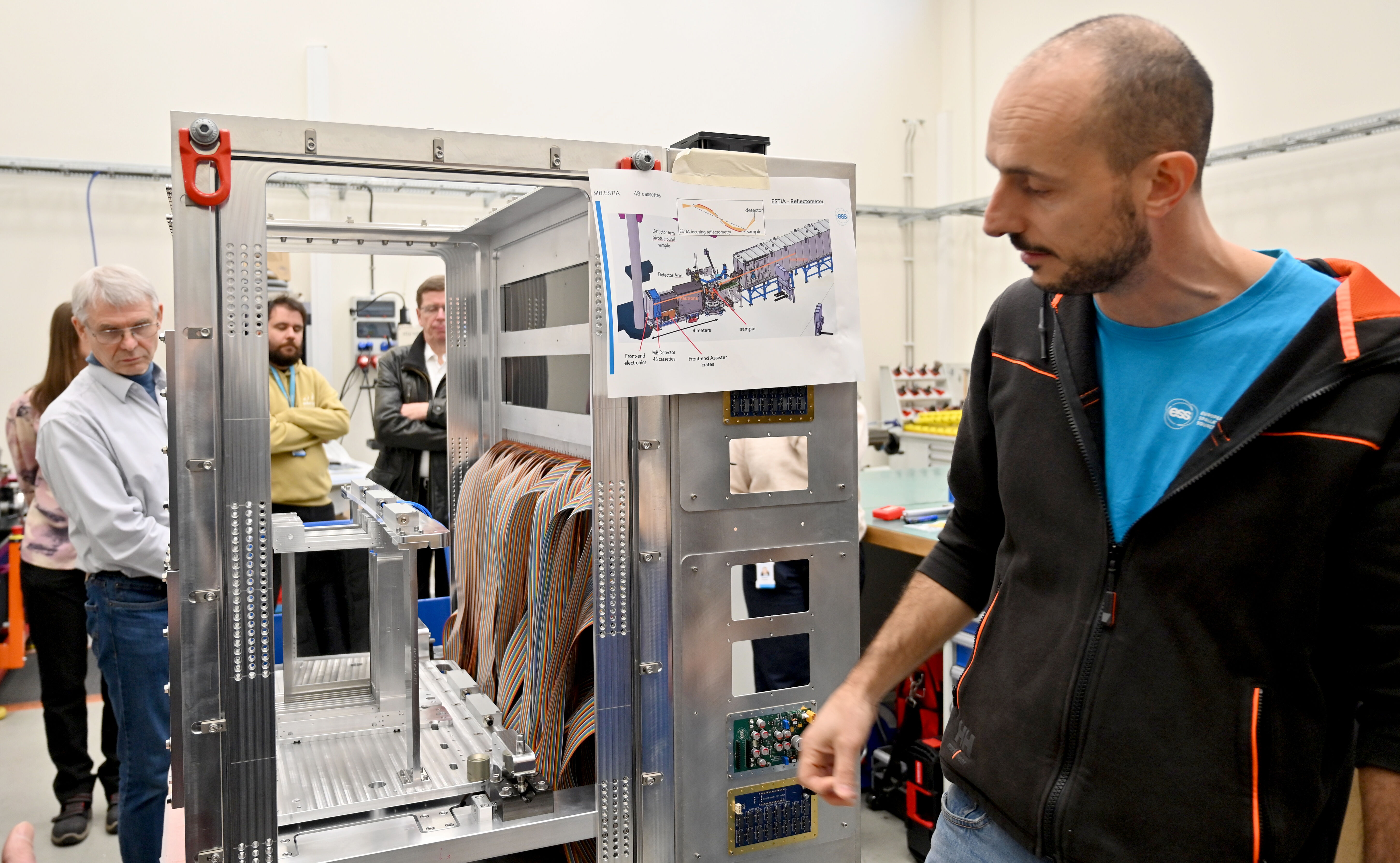
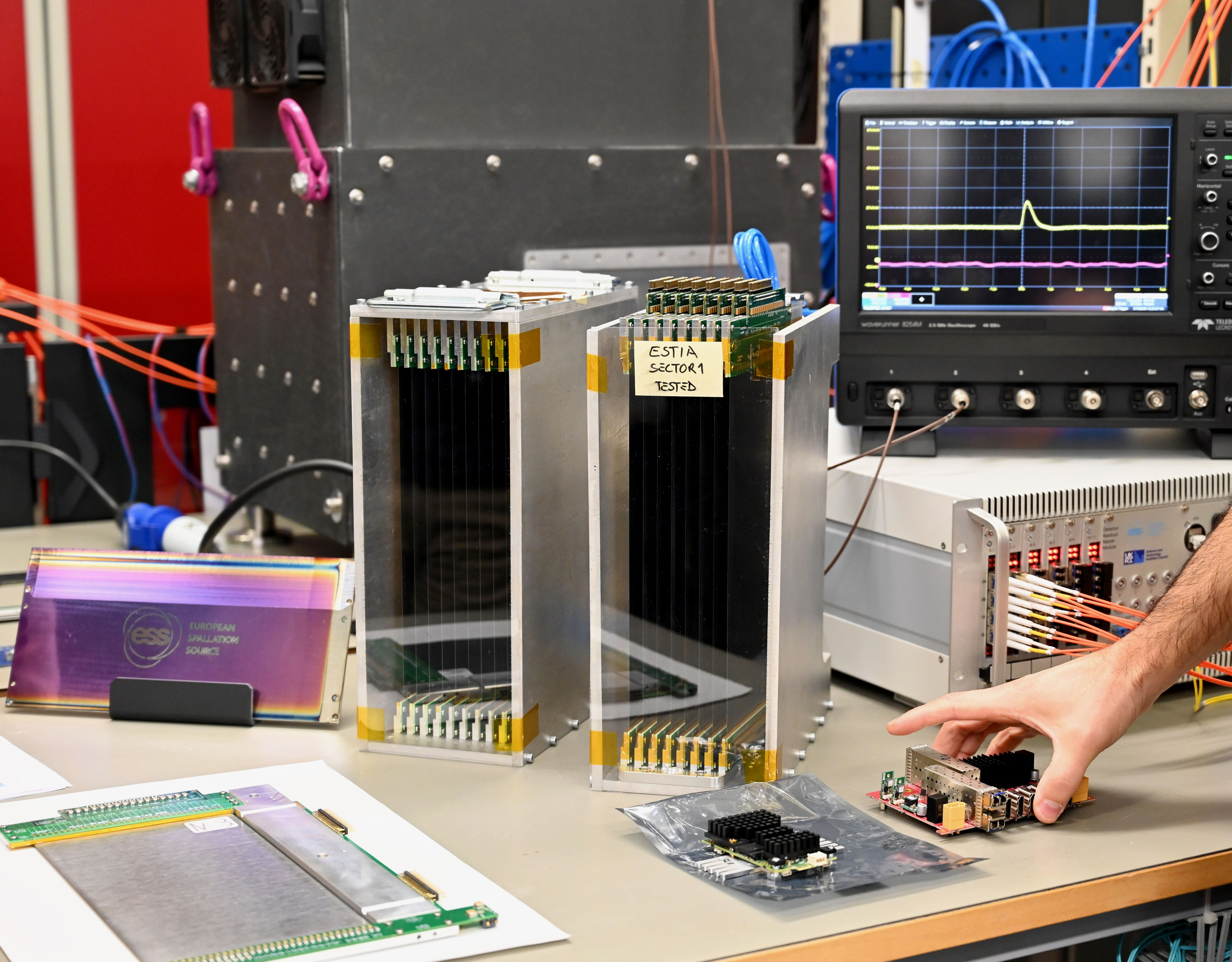
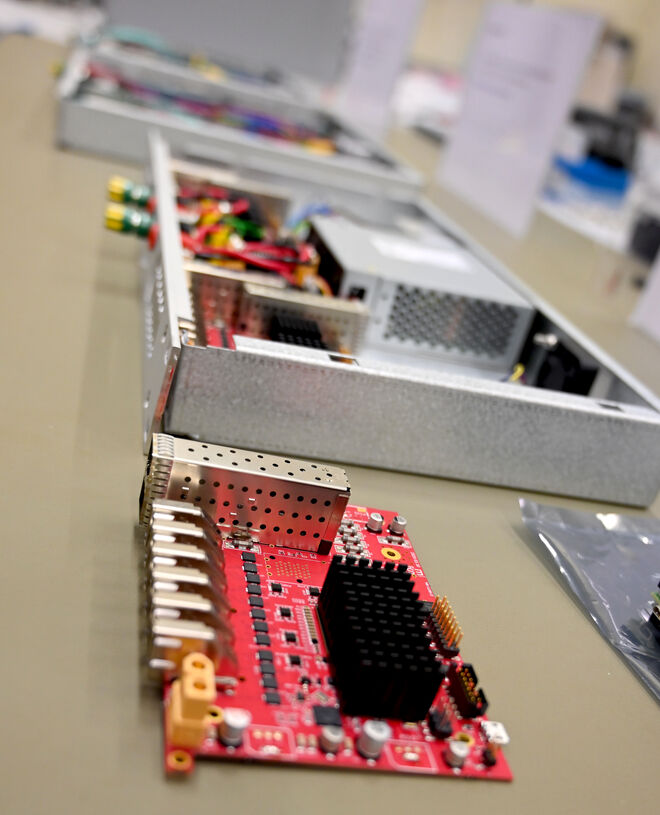
Among the innovations at Utgård are the advanced Multi-Blade detectors, specifically designed for neutron reflectometry instruments such as ESTIA and FREIA. These detectors incorporate novel technologies and a modular design, enhancing both spatial resolution and neutron counting rates. Such advancements enable a more detailed capture of scientific data, providing researchers with deeper insights into material structures and behaviours.
The Vital Role of Neutron Detectors at ESS
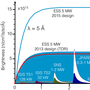
Neutron detectors are essential at ESS, enabling scientists to observe neutron interactions with samples under study. By recording neutron direction, speed, and interaction specifics, these detectors produce critical data that is sent to the ESS Data Management & Software Centre in Denmark for analysis and storage. The resulting data is then made accessible to scientists, offering a new level of detail in fields such as material science, structural biology and fundamental physics, driving significant advances in, for example, next-generation energy and data storage technologies as well as improved medical treatments.
What’s Next for Detector Installation at ESS
Detectors assembled and tested at Utgård are already installed or in the process of being integrated into several ESS instruments, including LOKI, DREAM, and BIFROST.
The remaining installations for the first-to-launch instruments are scheduled for completion this year, in preparation for the upcoming integrated cold commissioning phase early next year. This phase will bring together detector teams and other technical groups to ensure that the detectors come together in coherence with all the other parts of the instrument, achieving the performance specifications needed to drive significant scientific discoveries at ESS.