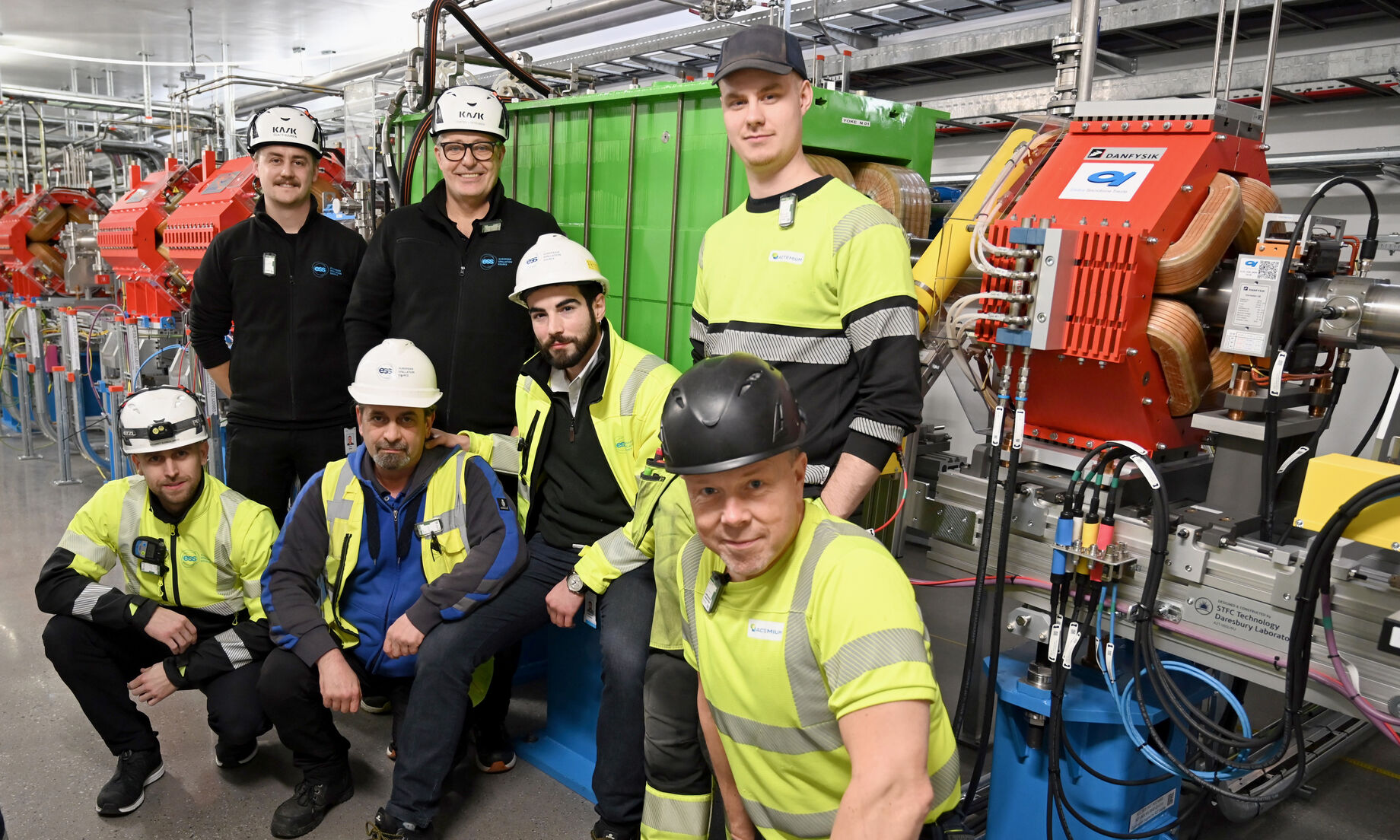
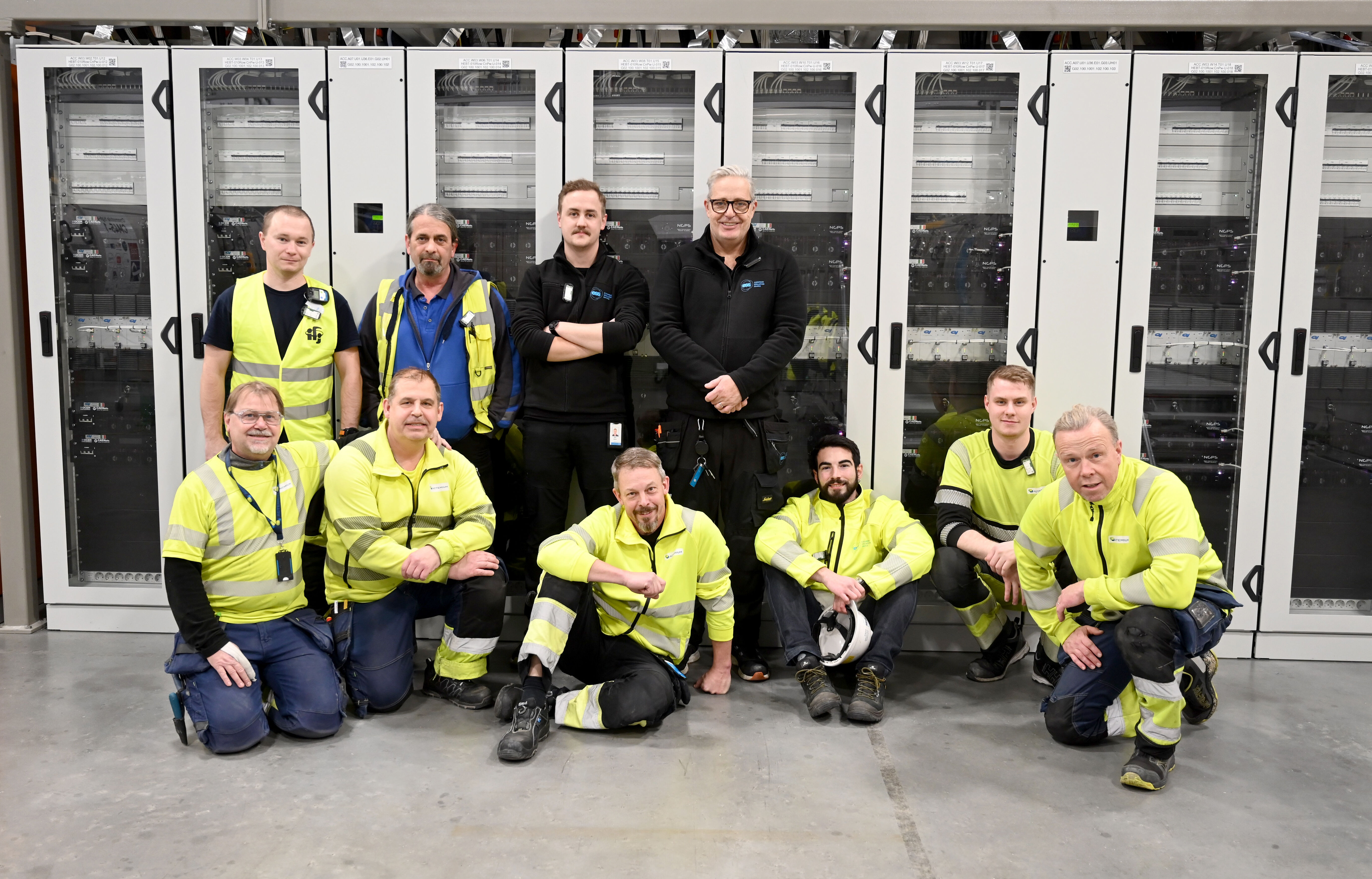
ESS has completed the integrated testing of all accelerator magnets. This achievement, following extensive preparation, marked the end of local and integrated testing phases of all magnets and power supplies required for commissioning the accelerator in early 2025 as well as for the Beam on Target (BoT) milestone.
A Long and Complex Testing Journey
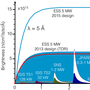
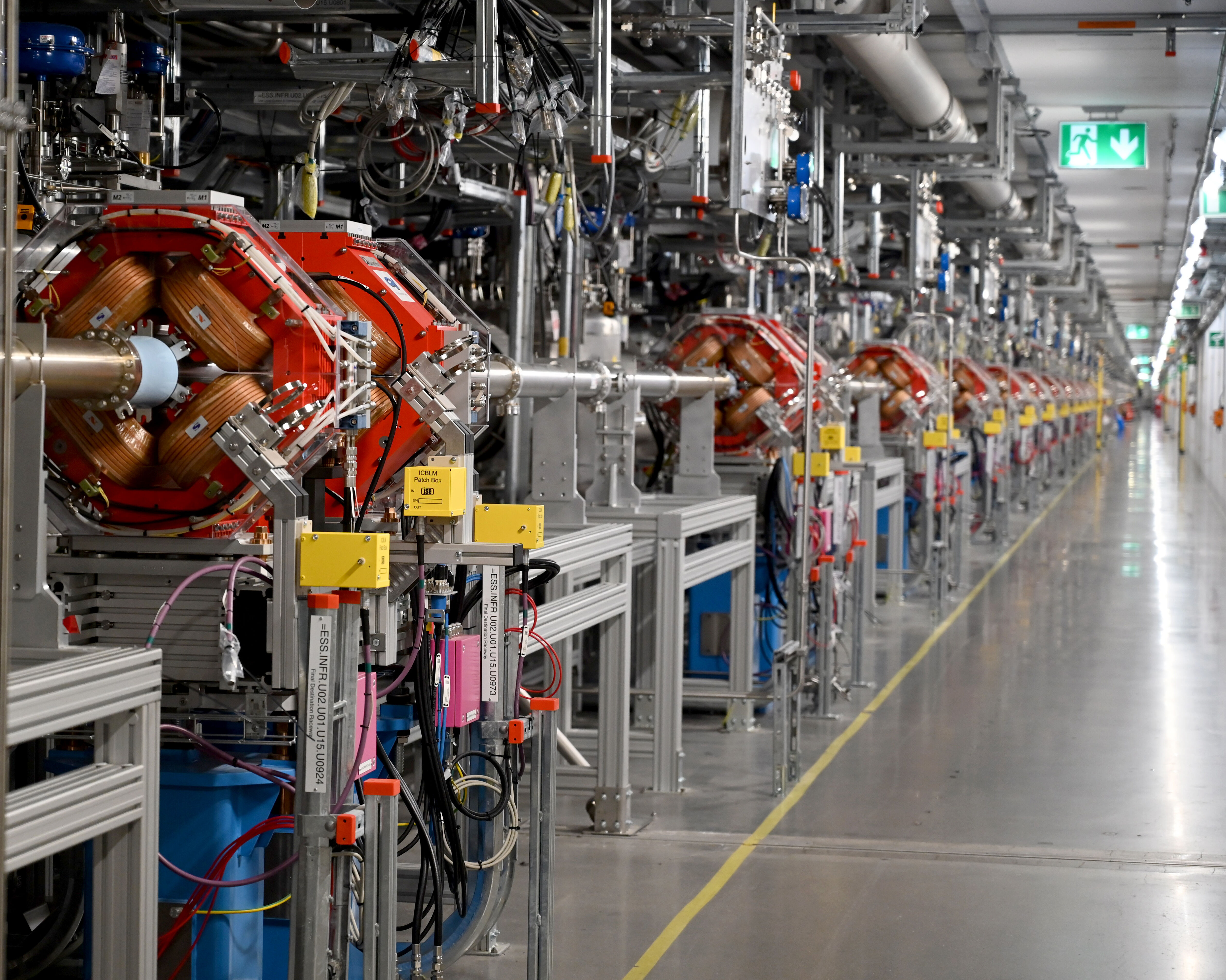
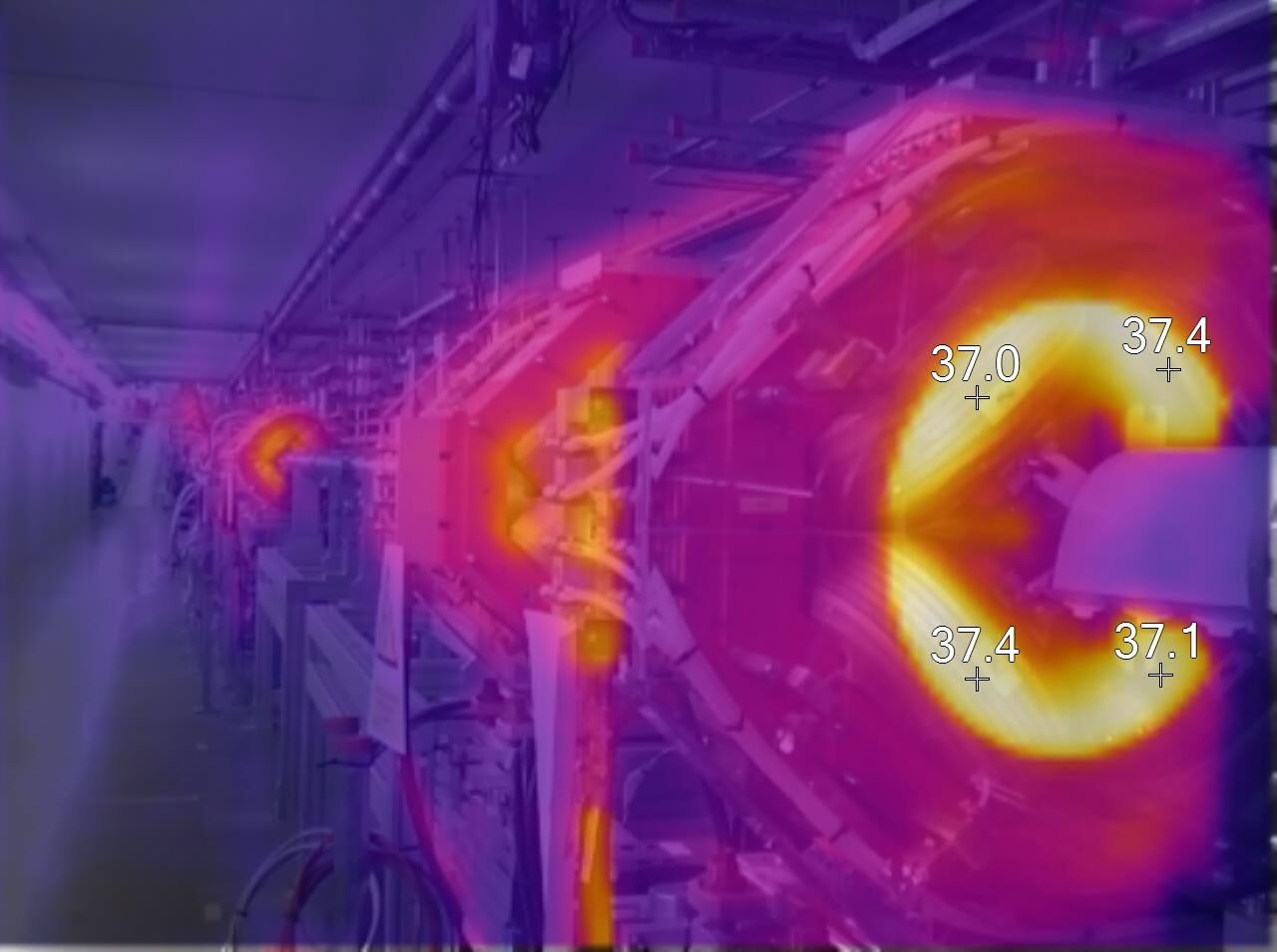
In early November 2024, the integrated testing phase concluded with all 213 magnets and 223 power supplies undergoing continuous 24-hour testing. These efforts involved power converters, controls, machine protection systems, cooling systems, and electrical interfaces.
The ESS magnets and their power converters is a significant In-Kind delivery from Elettra Sincrotrone in Trieste, Italy. Following Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT) by the supplier, the power converters underwent rigorous testing at the on-site Test Stand 3 and subsequently in their final positions using resistive loads during the Local Testing phase. During the following Integrated Testing phase, power converters were connected to the magnets for a series of power, thermal, interlock, and reliability tests.
The successful completion of both testing phases demonstrated the robustness and reliability of the entire system.
Advanced Magnet Systems at ESS
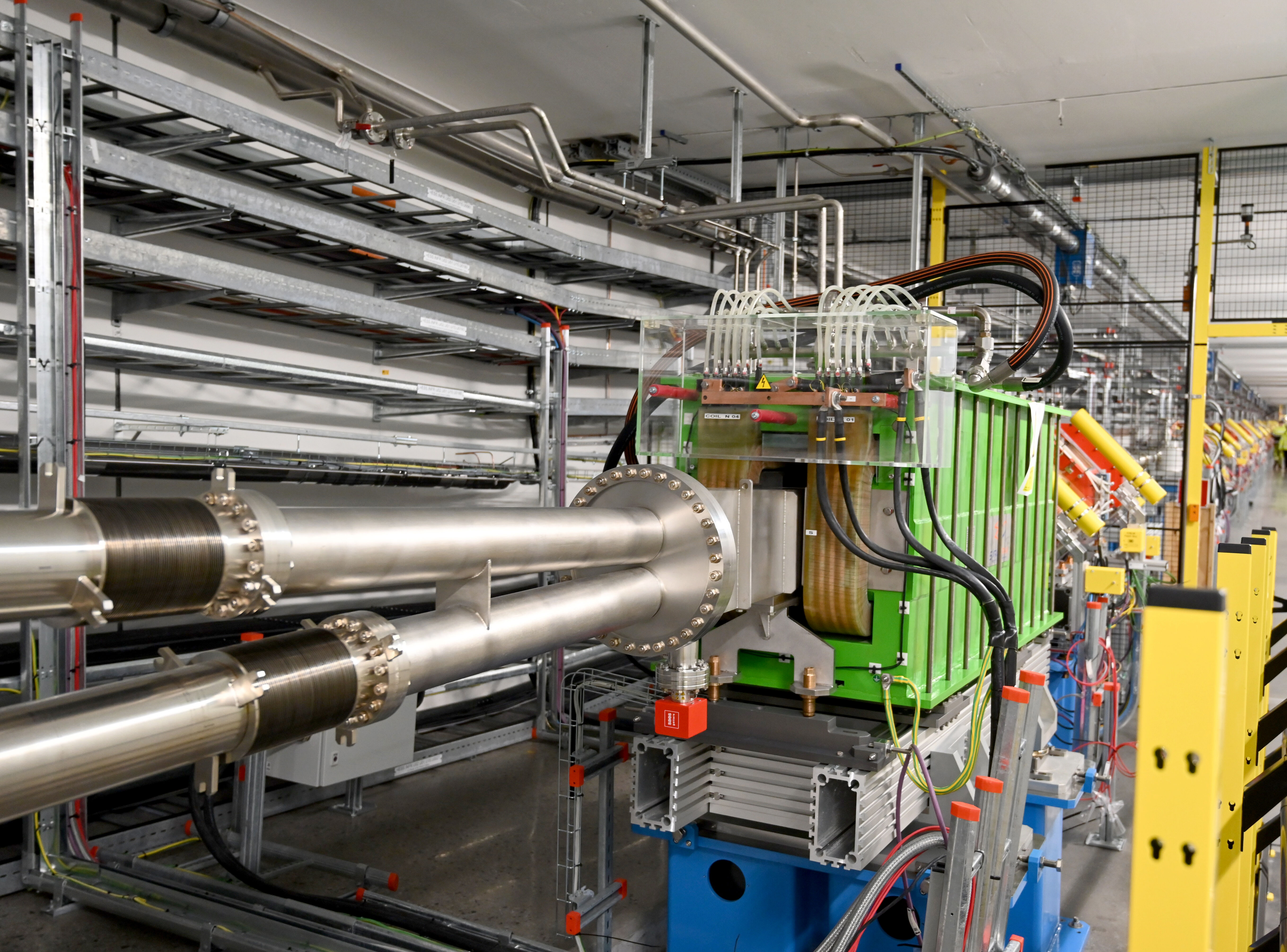
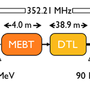
In a particle accelerator, magnetic fields are essential for focusing, steering, and bending particle beams. At ESS, four types of water-cooled quadrupole magnets focus the proton beam, while three types of air-cooled corrector magnets steer it. The magnets are strategically placed along the linac, including the Superconducting Linac (SCL), the High Energy Beam Transport (HEBT) line, the dumpline, and the Accelerator-To-Target (A2T) sections.
Each configuration includes two quadrupole magnets and one dual-plane corrector magnet, enabling precise beam transverse focusing and trajectory correction. Additionally, two vertical dipole magnets bring the beam from the accelerator tunnel level to the target level.
Cutting-Edge Power Systems
The magnets are powered by 39 racks of dedicated power converters located in the Klystron Gallery. These systems can deliver currents of up to 400 A per magnet, generating the required magnetic fields. To streamline operations, a high level of standardisation was achieved, including the use of a uniform conductor cross-section and current density across systems.
While quadrupole and dipole magnets use commercial off-the-shelf power converters, the corrector magnets required custom solutions developed in collaboration with In-Kind Partner Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste.
Collaborative Efforts and International Contributions
This achievement reflects the collective efforts of ESS’s Linac, Power Converters, Vacuum, Integrated Control Systems (ICS), and Machine Protection System (MPS) teams, alongside the invaluable contributions from Italian in-kind partner Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste.
Paving the Way for Beam Operations
The successful testing of these complex systems lays a solid foundation for upcoming milestones, including Beam on Dump (BoD) and Beam on Target (BoT). Accelerator Project Manager Ciprian Plostinar commended the achievement, stating:
"Seeing this complex system fully tested and ready for beam gives me confidence that we’re delivering excellence on multiple fronts—technical, collaborative, and project management. Congratulations to everyone who contributed to this achievement. Your hard work brings us one step closer to BoD and BoT."
This milestone not only highlights the technical sophistication of the ESS accelerator but also celebrates the commitment and collaboration of the teams and partners driving the project forward.
This spotlight article is part of the series "Road to Beam on Dump" where we highlight all the systems required to commission the ESS accelerator.
Previous updates:
- Warm Coupler Conditioning Completed - ESS Accelerator Prepares for Cold Operation
- ESS Linac Under Vacuum
- The Power to Accelerate: RF Power Stations up and running
- Installation and Testing of the 2 MW RF Scope Completed
- Focus on Beam Instrumentation: Completion of Beam Current Monitors Installation in the ESS Accelerator
- First Insertable Beam Stop installed in the ESS superconducting linac
- Magnets Ready to Focus and Steer the Proton Beam
- Warm Coupler Conditioning starts in the ESS Superconducting Linac