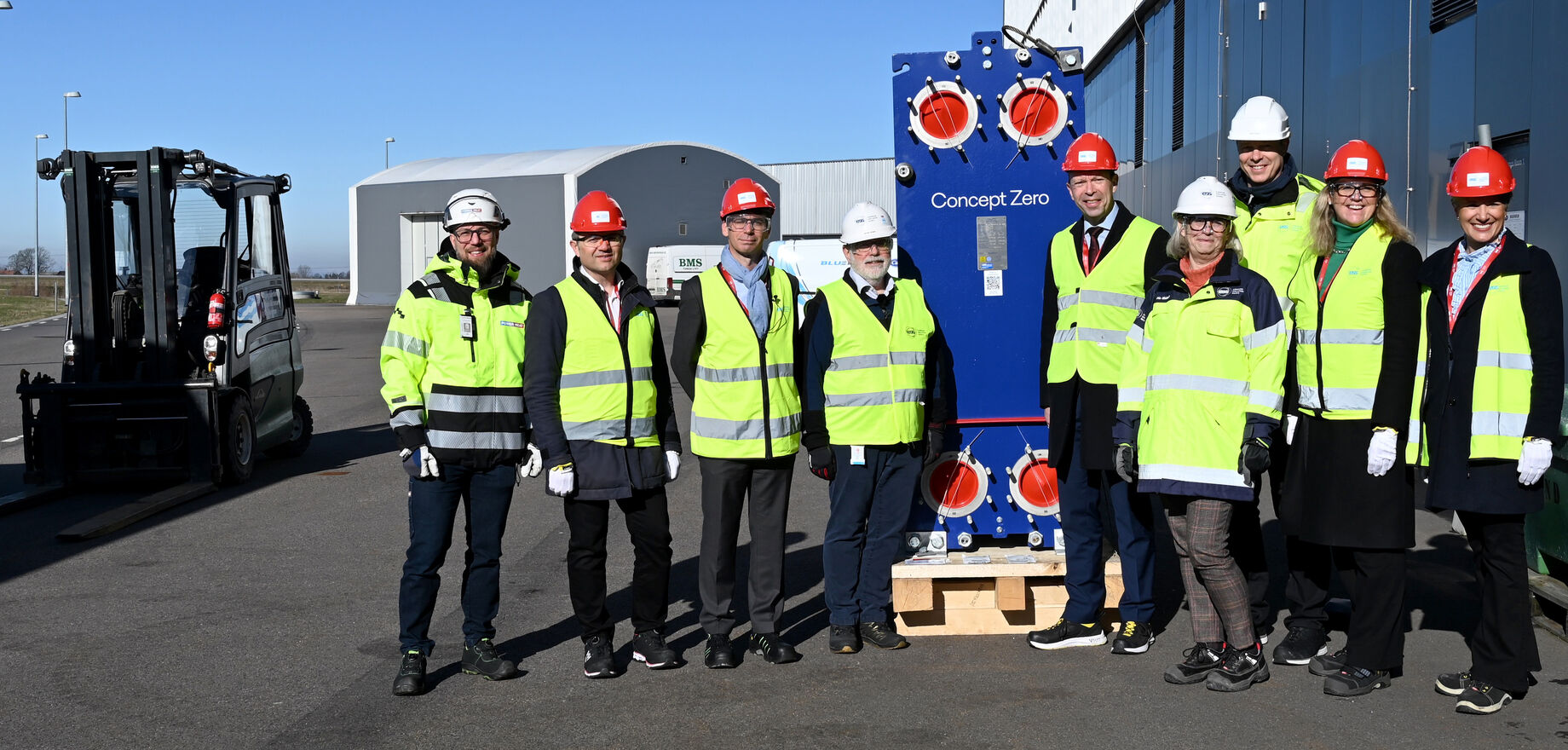
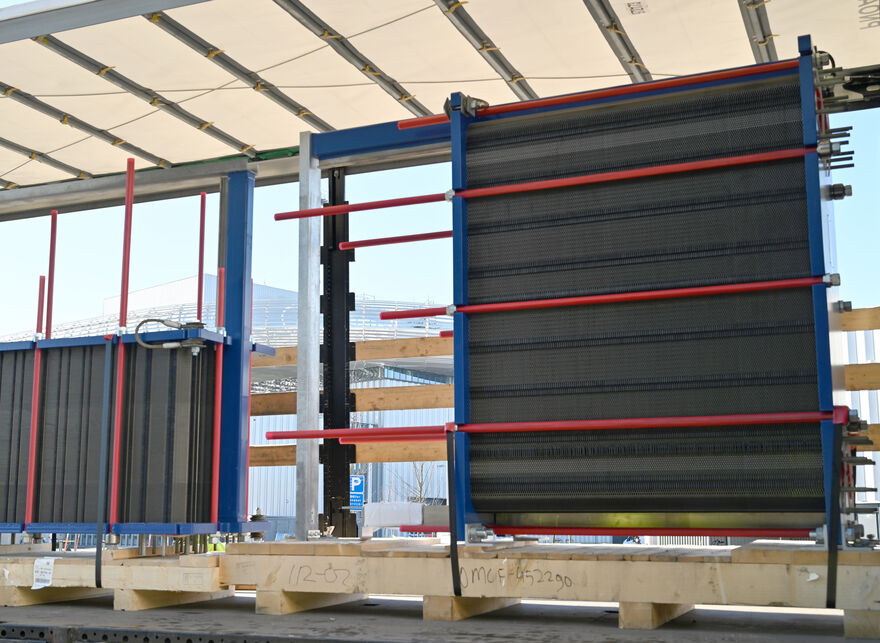
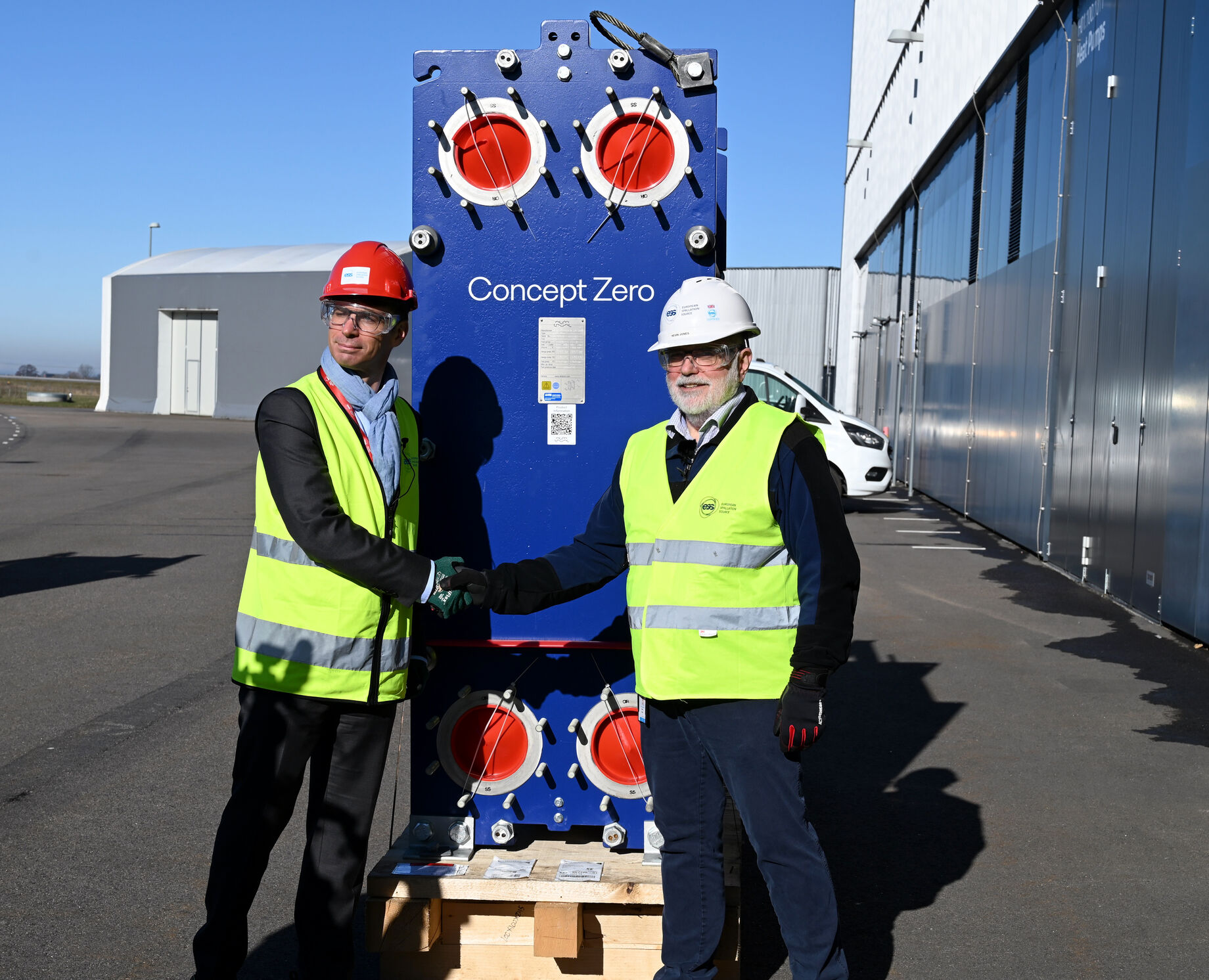
On 8 March ESS welcomed the delivery of the world's first net-zero steel heat exchanger from Alfa Laval, setting a new standard for sustainable energy solutions.
The delivery of the world's first net-zero steel heat exchanger to ESS by Alfa Laval on 8 March 2024 marks a step forward in sustainable energy solutions and reducing industrial carbon footprints. This pioneering development, produced by Alfa Laval using recycled carbon steel from Swedish steel manufacturer SSAB, represents a key contribution to the global effort to decrease the CO2 emissions associated with steel production, which accounts for approximately 10% of worldwide CO2 emissions.
The recycled carbon steel, produced by SSAB in an electric furnace using renewable energy, signifies the beginning of environmentally friendly steel manufacturing. This approach paves the way for a future where all steel is net-zero by combining HYBRIT's green steel technology with recycled resources.
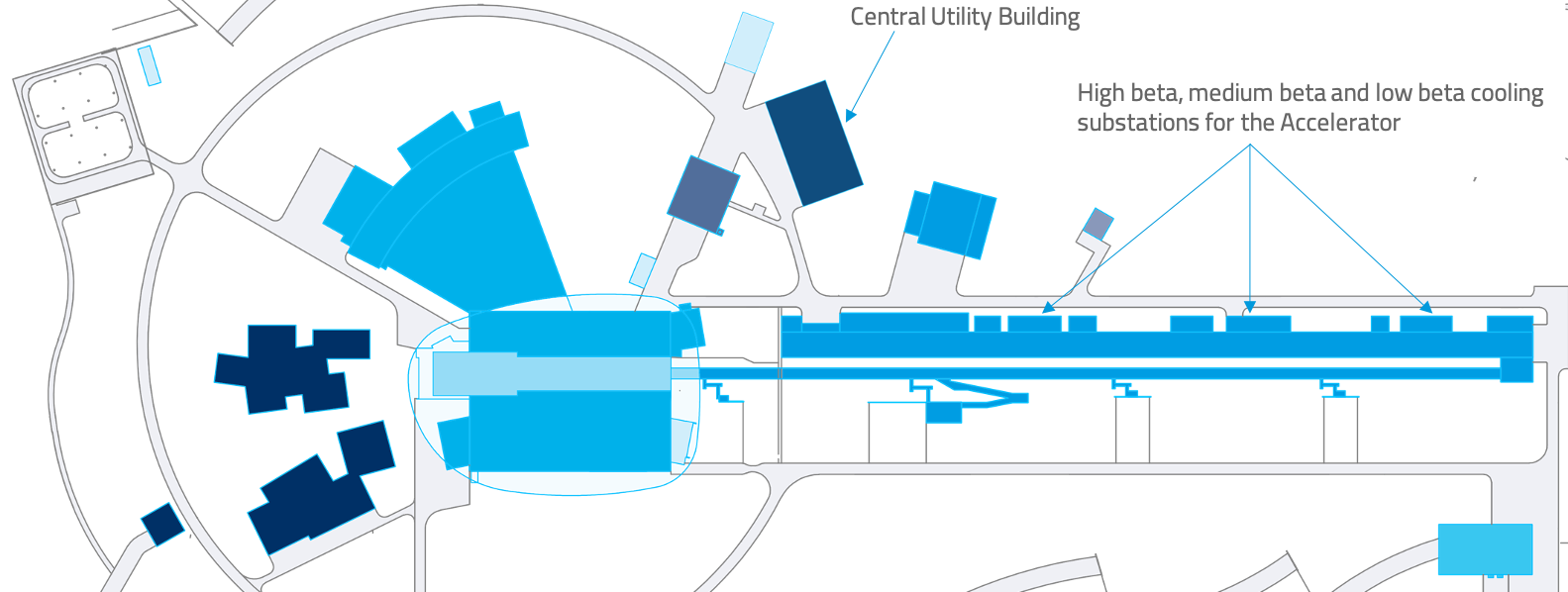
The eco-friendly heat exchanger will be installed in the ESS accelerator’s medium beta cooling substation. While its primary role is to cool the Accelerator systems at ESS, it is also linked to the Central Utility Building’s heat recycling system, which sends surplus heat from ESS into Lund’s district heating network, covering the heating needs of the roughly 40,000 people expected to live and work in the Brunnshög district in northeastern Lund.
While the high beta substation upgrades have been completed using conventional heat exchangers, the installation of the net-zero steel heat exchanger in the medium beta substation begins a new chapter in sustainable cooling solutions.
Part of the low-temperature district heating network in Lund
This innovation aligns with the broader goals of expanding low-temperature district heating (LTDH) networks. The LTDH network in Lund, inaugurated in 2019, is set to become Europe's leading test field for sustainable heating solutions, partially funded by the EU's Horizon 2020 program. Alfa Laval's supply of ConceptZero heat exchangers to this network, including the emission-free steel unit for ESS, underscores the critical role of sustainable technologies in achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, as projected by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The partnership between Alfa Laval, ESS, and other stakeholders demonstrates a collective commitment to advance technologies to drive the energy transition.
“We are proud to be part of this initiative. Taking measures for sustainability fully resonates with the mission of our facility, where research in material and life sciences will contribute to addressing global challenges,” says ESS Director General Helmut Schober.
Read more about this collaborative effort on the Alfa Laval website.