ODIN
Multi-Purpose Imaging
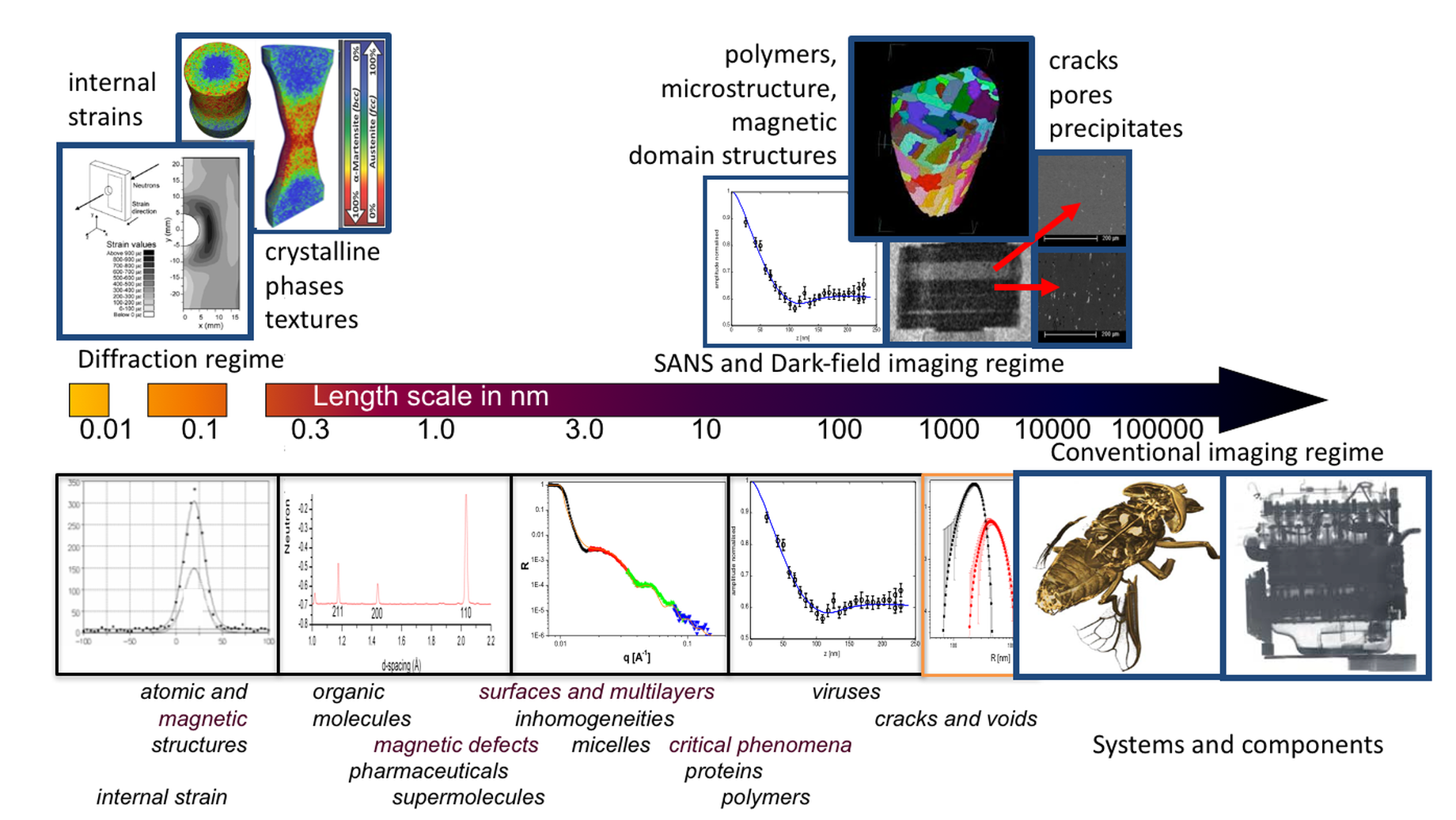
ODIN is a multi-purpose imaging instrument intended to satisfy a wide range of scientific needs in a variety of fields such as engineering materials and components, geo-science, palaeontology and much more. It will provide spatial resolutions down to the µm‑range enabled by the high brightness of ESS coupled with ongoing advances in detector technology. The pulsed nature of the source will give access to wavelength-resolved information, yielding a qualitative informational advance over current state-of-the-art. The full scope capability offers its users a variety of imaging techniques for the characterisation of objects with applications in virtually all natural science disciplines.
Instrument Class
Beam Port
Lead Scientist
Lead Engineer
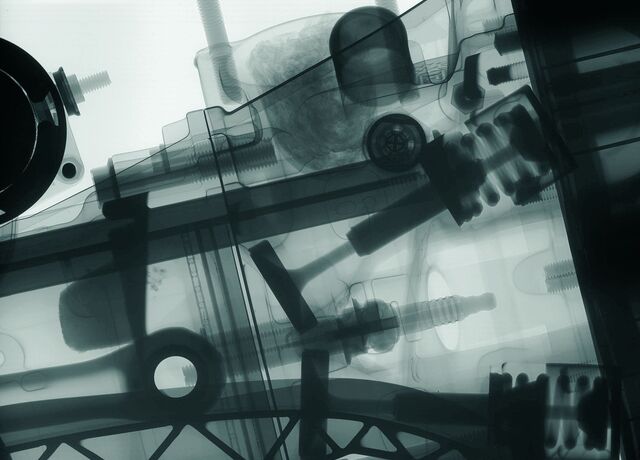
Neutron imaging is a real-space technique examining the inner structure of potentially highly complex components and samples by detecting the transmitted beam.
ODIN’s multi-purpose imaging capability provides spatial resolutions down to the µm‑range enabled by the high brightness of ESS coupled with ongoing advances in detector technology. The pulsed nature of the source will give access to wavelength-resolved information, yielding a qualitative informational advance over current state-of-the-art instruments.
The full scope capability offers its users a variety of imaging techniques for the characterisation of objects with applications covering, but not limited to, cultural heritage, energy materials and devices, magnetic phenomena, biology, geology, food science and in industrial applications e.g. fuel cell development, rechargeable battery development and non-destructive inspection of engineering components.
Different imaging techniques, from traditional attenuation-based imaging to advanced dark field, polarized neutron or Bragg edge imaging, will be available within the full scope of ODIN with unprecedented efficiency and resolution. (See [1] and references therein for a review of imaging techniques as well as [2] for a newly developed dark field technique.) The instrument concept prepared to host the full scope takes full advantage of the flexibility made possible by the ESS time structure, allowing wavelength resolution, bandwidth and collimation to be tailored to each application.
As a multi-purpose imaging instrument ODIN is designed to satisfy a wide range of scientific needs. Given the plethora of applications in various scientific fields, only a few examples can be given here:
- Energy research and environment – e.g energy storage devices (batteries, fuel cells etc.), catalysis, nuclear energy materials.
- Magnetism and condensed matter research – e.g high density data storage materials, energy efficient magnetic materials in engineering applications, superconductivity.
- Engineering materials – study of strains, stresses, textures and microstructures deep in metal components.
- Geology, earth and agricultural sciences – structural information in rocks, sands and soil. Allowing for studies of e.g water transport mechanism in ground fractures, CO2 storage in the ground, compaction and movement of sandy grounds, soil transport characteristics in large-scale earthquakes and continental shifts, studies of root growth and function in soil.
- Soft matter and biology – e.g study microstructural details and transitions in biology along with soft matter investigations and externally triggered transitions in soft matter, study of systems like full plants.
- Archeology, Paleontology and Cultural heritage – enhancement of today’s capabilities with respect to structures and microstructures of ancient tools, weapons, fossils and artworks. Providing better understanding of e.g ancient metallurgy and fabrication methods.
- Routine Non-destructive Evaluation of Material Reliability – e.g study of component failure and improved welding processes, product development and improvement, creep detection.
[1] N. Kardjilov et al.: Neutron Imaging in Materials Science, Materials Today, 14 (6), p 248, 2011
[2] M. Strobl et al.: Quantitative Neutron Dark-field Imaging through Spin-Echo Interferometry, Scientific Reports, 5, 16576 (2015)
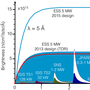
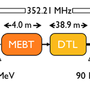
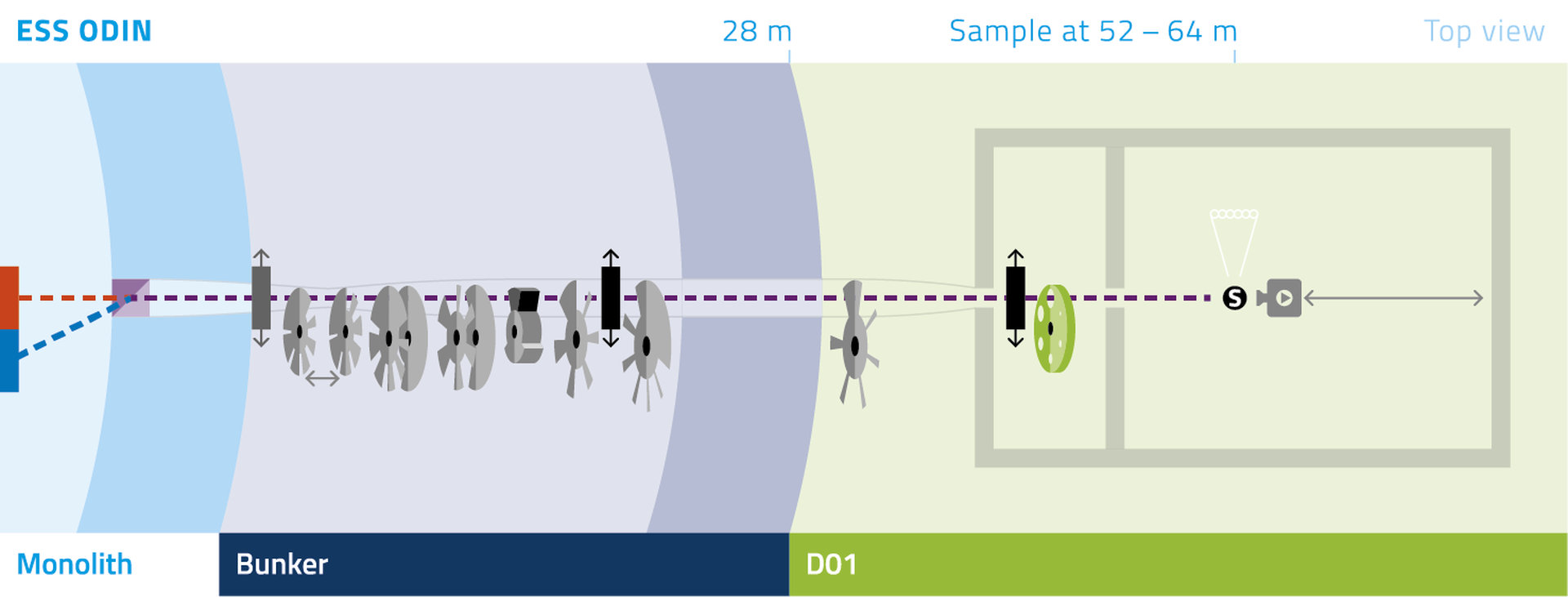
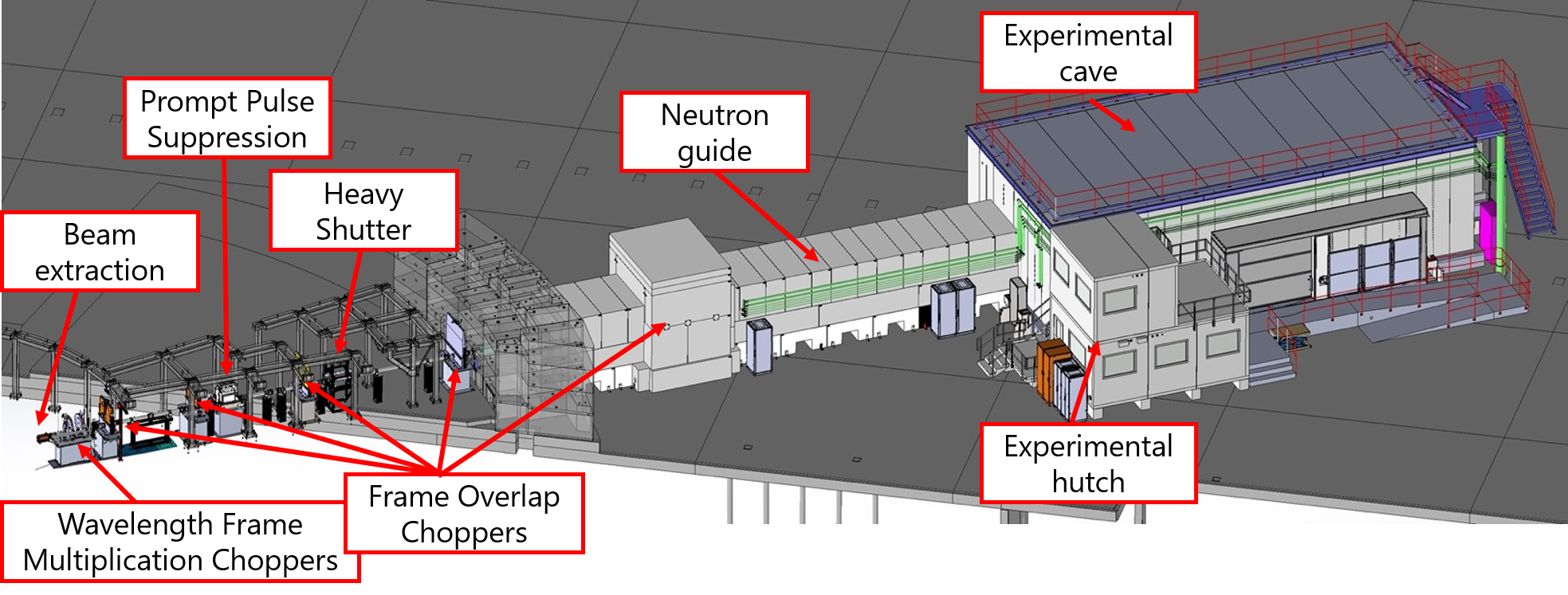
The total length of the instrument from source to sample is 60 m. This ensures that the lowest required Time of Flight (TOF) resolution of about 10% is achieved for 2Å, given the source pulse length of 2.86 ms.
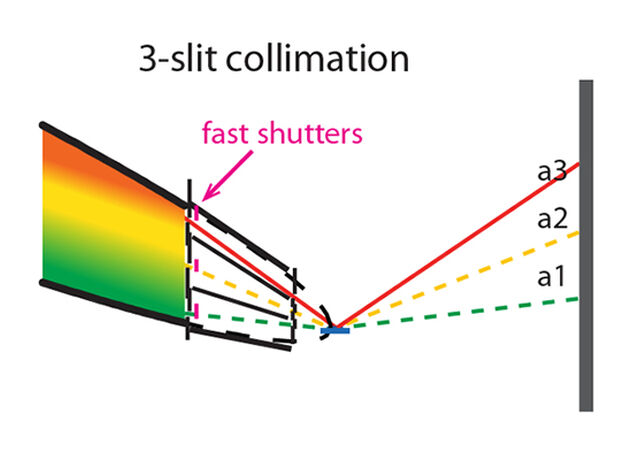
In order to achieve better TOF resolutions, required for example for many Bragg edge studies, a wavelength frame multiplication chopper (WFMC) system is foreseen. This system is based on a moveable pair of optical blind pulse shaping choppers for constant wavelength resolution. At the long pulse source they are combined with frame overlap choppers (FOC).
Changing the distance between the pulse shaping choppers allows for tuning the resolution. In order to tune to high resolutions the beam cross section at the pulse shaping choppers just outside the target monolith has to be limited. Therefore an eye-of-the-needle approach, where the beam is focused between these two choppers is taken.
A second focal spot of the guide at 50 m from the moderator followed by an up to 10 m long flight path in front of the detector position defines the imaging geometry, achieving the maximum desired Field of View (FOV). Additionally, the instrument takes advantage of the bi-spectral extraction opportunity at ESS in order to use the full available bandwidth ranging from 1Å (e.g. Bragg edge strain mapping to well above 10Å. See [3] and references therein for a more detailed description of the design rationale.
Sample Environment
ODIN will have access to the common pool of sample-environment equipment provided by ESS.
Publications
Andersen, K. H. et al. The instrument suite of the European Spallation Source. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section a-Accelerators Spectrometers Detectors and Associated Equipment 957, 39, doi:10.1016/j.nima.2020.163402 (2020).
Kardjilov, N., Manke, I., Woracek, R., Hilger, A., Banhart, J. Advances in neutron imaging. Materials Today (2018).
Woracek, R., Santisteban, J., Fedrigo, A., & Strobl, M. Diffraction in neutron imaging — A Review. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment (2018), 878, 141-158.
M. Strobl et al.: Quantitative Neutron Dark-field Imaging through Spin-Echo Interferometry, Scientific Reports, 5, 16576 (2015)
M. Strobl: The Scope of the Imaging Instrument Project ODIN at ESS, Physics Procedia 69, p 18, 2015
M. Strobl, F. Grazzi: From Scattering in Imaging to Prospects at Pulsed Sources, Neutron News (2015) 26:2, 23-26, DOI: 10.1080/10448632.2015.1028275
N. Kardjilov et al.: Neutron Imaging in Materials Science, Materials Today, 14 (6), p 248, 2011
Lead Scientist
Robin Woracek, ESS
Construction Lead Scientist
Aureliano Tartaglione, TUM, Germany
Installation Package Leaders
Virginia Martinez Monge, TUM, Germany
Egla Luca, ESS
Commissioning Scientist
Stefanos Athanasopoulos, ESS
Instrument Data Scientist
Søren Schmidt, ESS
Instrument Operations Engineer
Richard Ammer, ESS
Lead Engineer
Bojan Peric, ESS